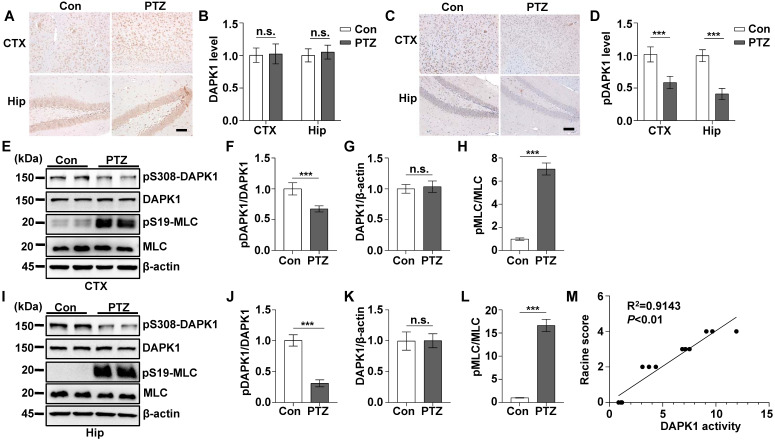
Figure 1.
Acute PTZ administration increases DAPK1 activity. Mice (C57BL/6, male, P56-P80, n = 8/group) were administered a convulsive dose of PTZ (50 mg/kg), and brain tissues were harvested 3 min after PTZ injection. A-D Immunohistochemistry using an anti-DAPK1 (A) and anti-pSer308-DAPK1 (C) antibodies was conducted on paraffin-embedded cortical and hippocampal sections from the control and PTZ-treated mice. Scale Bar = 100 µm. Quantitation of DAPK1 (B) and pSer308-DAPK1 (D) staining intensity (arbitrary units; two-tailed Student's t-tests). E-L Cortical and hippocampal lysates were subjected to immunoblotting analysis with anti-pSer308-DAPK1, anti-DAPK1, anti-pSer19-MLC, anti-MLC or anti-β-actin antibodies (***P < 0.001 vs control; two-tailed Student's t-tests). M Correlation between the Racine score on the Y axis and DAPK1 activity on the X axis based on the pSer19-MLC level (R2 = 0.9143, P < 0.01, Pearson correlation coefficient). n.s., no significance. All data shown represent the means ± standard errors of three independent experiments.