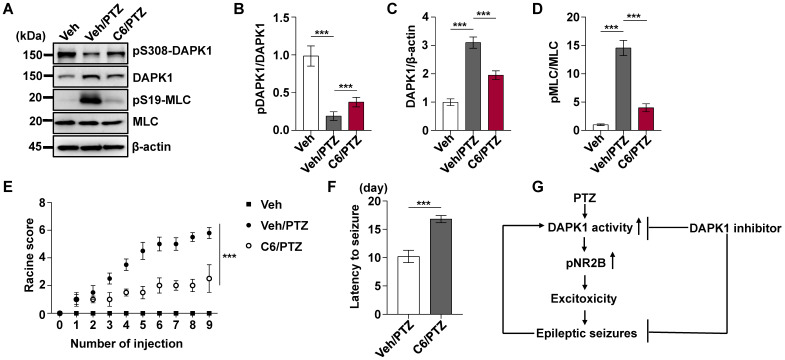
Figure 6.
Pharmacological inhibition of DAPK1 reduces the development of epilepsy in PTZ-induced kindling. Mice (C57BL/6, male, P56-P80, n = 12/group) were pretreated with a DAPK1 inhibitor (10 mg/kg) or vehicle for 5 min followed by a subconvulsive dose of PTZ (35 mg/kg) every other day (nine injections for 17 days). The brain tissues from a number of the animals (n = 4) were harvested after the fourth PTZ injection, and the remaining animals continued to undergo behavioral analysis. A-D DAPK1 inhibitor pretreatment decreased DAPK1 activity after chronic PTZ exposure. The brain lysates were subjected to immunoblotting analysis with anti-pSer308-DAPK1, anti-DAPK1, anti-pSer19-MLC, anti-MLC or anti-β-actin antibodies. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons tests (***P < 0.001). E Mean seizure grades of PTZ-kindled WT treated with vehicle or C6, with lower seizure grades were noted in the DAPK1 inhibitor-treated mouse group (***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). F Latency to the first kindled seizure was significantly prolonged in the DAPK1 inhibitor pretreatment mouse group (***P < 0.001 vs vehicle, two-tailed Student's t test). All data shown represent the means ± standard errors of three independent experiments. G Schematic diagram summarizing the proposed role of DAPK1 in epilepsy.