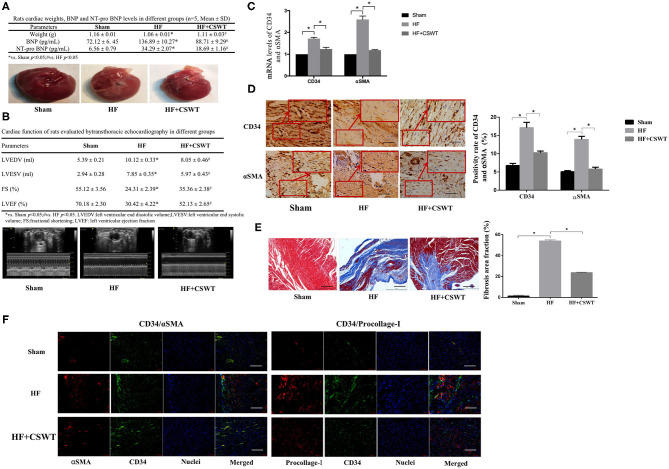
Figure 1.
CSWT improves cardiac functions and reduced fibrosis in rats with post-AMI HF. (A) The cardiac weight, serum levels of BNP and NT-pro BNP and gross view of whole hearts in study groups; (B) Representative M-mode images by echocardiography of rats in study group; (C) Fold changes in CD34 and αSMA mRNA levels determined by RT-PCR in study groups; (D) The positive rates of CD34 and αSMA in study groups using Immunochemistry analyses; scale bar, 100 μm; (E) Representative images of Masson's trichrome staining and quantification for fibrosis of rat hearts from each group; scale bar, 100 μm; (F) Representative photomicrographs of immnunofluorescence for the detection of CD34/αSMA and CD34/Procollage-I. Red fluorescence shows αSMA or Procollage-I expression. Green fluorescence shows CD34 expression. Blue fluorescence shows nuclei of total cardiomyocytes; scale bar, 50 μm. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M (n = 5). One-way ANOVA test was applied for determining the significance of data. *p < 0.05. CSWT, cardiac shock wave therapy; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; HF, heart failure; S.E.M, standard error of means.