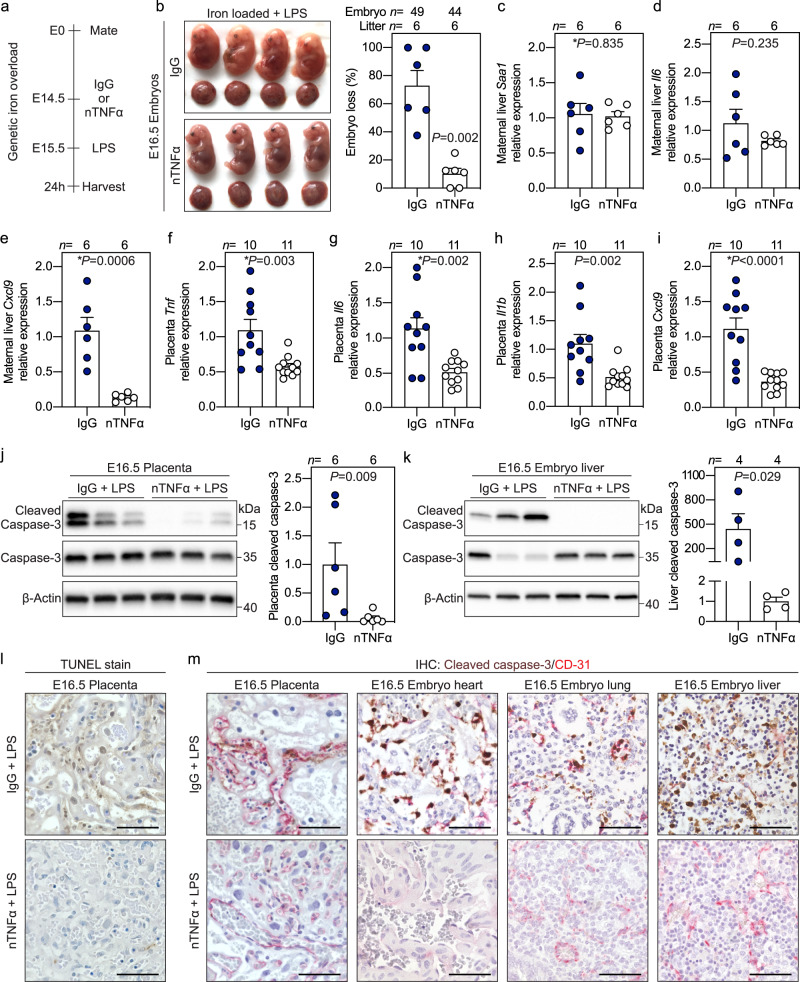
Fig. 3. Synergistic toxicity of iron and inflammation is mediated by maternal TNFα.
a Iron-loaded hepcidin KO dams were treated intravenously via the retroorbital sinus with 500 μg neutralizing TNFα antibody (nTNFα, white circles) or isotype control IgG (IgG, blue circles) neutralizing trinitrophenol 15 h prior to subcutaneous injection of LPS (0.5 μg/g) on E15.5 for 24 h. b Gross morphology and incidence of resorbing embryos. c–e Maternal liver expression of inflammatory markers Saa1, Il6, and Cxcl9 normalized to Hprt. f–i Placental mRNA expression of inflammatory markers Tnf, Il6, Il1b, and Cxcl9 normalized to Rpl4. j, k Western blots and quantitation of whole placenta or embryo liver lysates for cleaved caspase-3 expression normalized to β-actin. l TUNEL stain of placental sections. m Immunohistochemistry for cleaved caspase-3 (brown) and CD31 (red) in paraffin-embedded placenta, embryo heart, lung, and liver. l, m Representative images of n = 3 sections/group. Scale bar = 50 μm. f–m Embryo and placentas were randomly selected for analysis. c–k Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. Statistical differences between groups were determined by two-tailed Mann–Whitney U or two-tailed Student’s t-test (denoted by *). P-values are indicated in each figure panel. Source data are provided as a Source data file.