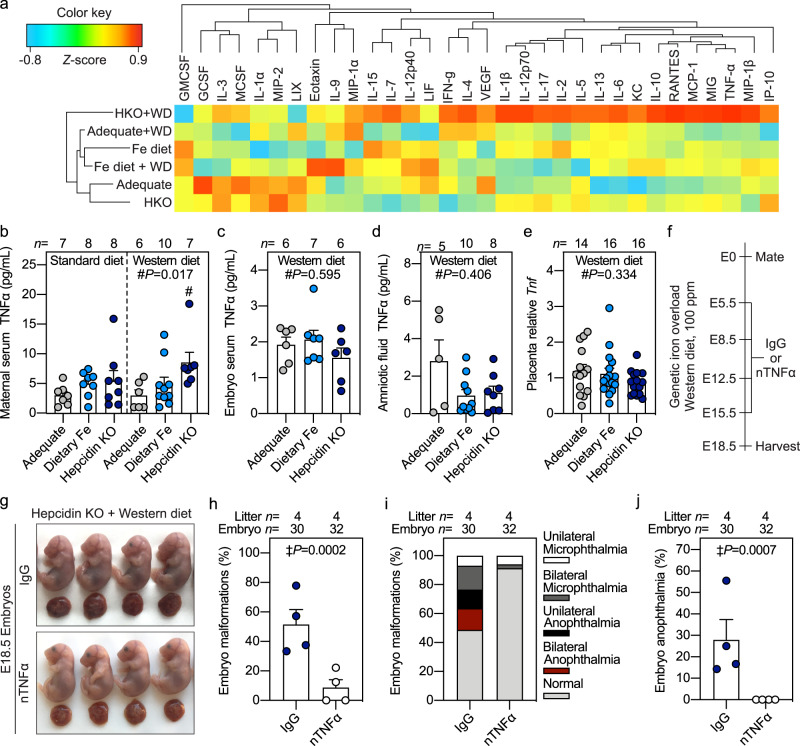
Fig. 7. Neutralizing maternal TNFα is protective against embryonic malformation induced by the combination of high maternal iron and Western diet.
a Clustering analysis of 32-plex cytokine panel in maternal serum from iron-adequate (gray circles), dietary iron-loaded (Fe diet, light blue circles), and genetically iron-loaded hepcidin KO (HKO, dark blue circles) dams fed standard or Western diet (WD). Color key indicates Z-score for each cytokine. b–e E18.5 TNFα measurements in b maternal serum, c embryo serum pooled from each litter, d pooled amniotic fluid, and e placental Tnf gene expression. Placentas were randomly selected for analysis. f Hepcidin KO females were fed Western diet (100 ppm iron) starting at 3 weeks of age and were mated after 9 weeks. Pregnant dams received intravenous injections of neutralizing TNFα antibody (white circles) or isotype IgG (dark blue circles) targeting trinitrophenol as a control (250 µg/injection) on E5.5, E8.5, E12.5, and E15.5, and embryo outcome was evaluated at E18.5. g Embryo gross morphology. h–j Incidence of eye malformations. b–e, h, j Error bars represent mean ± s.e.m. Statistical differences were determined by one-way ANOVA on ranks followed by Dunn’s method for multiple comparisons (denoted by #) or two-tailed Fisher’s exact test (indicated by ‡). P-values are indicated in each figure panel. Source data are provided as a Source data file.