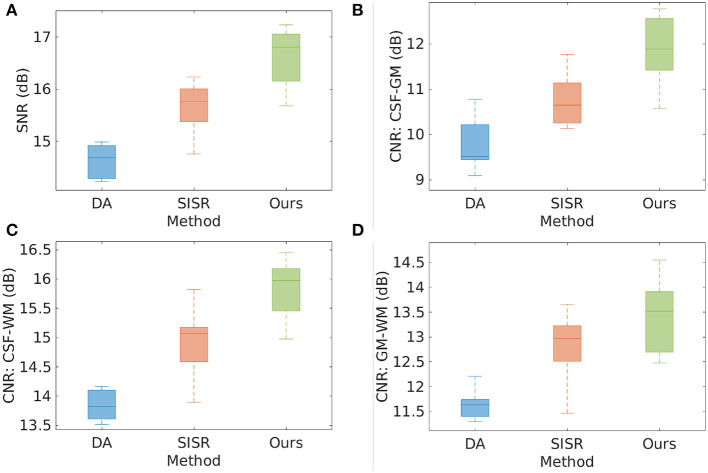
Figure 3.
Results of direct acquisition (DA), SISR, and our approach in terms of SNR and CNR from the eight MPRAGE acquisitions/reconstructions from the simulated data set. (A) The average SNRs obtained from DA, SISR, and our approach were 14.51 ± 0.57, 15.66 ± 0.48, and 16.62 ± 0.56 dB, respectively. Our approach achieved higher SNR on this data set, and yielded 2.11 dB enhancement in SNR as compared to direct acquisition. Two-sample t-test at the 5% significance level showed that our approach significantly outperformed DA (p = 3.02e−6) and SISR (p = 2.40e−3). Wilcoxon signed-rank tests, where the null hypothesis was the difference of two sets of data comes from a distribution with zero median, showed that the population mean rank of our approach significantly differed from the two baselines in SNR at the 5% significance level (rejected the null hypothesis with p = 7.8e−3 for both DA and SISR). (B–D) Our approach consistently offered the highest CNRs between the three types of brain tissues on this data set. In particular, our approach achieved 1.31 dB higher CNR between GM and WM than direct acquisition. The results show that SRR led to considerably improved SNR and CNR as compared to direct HR acquisition.