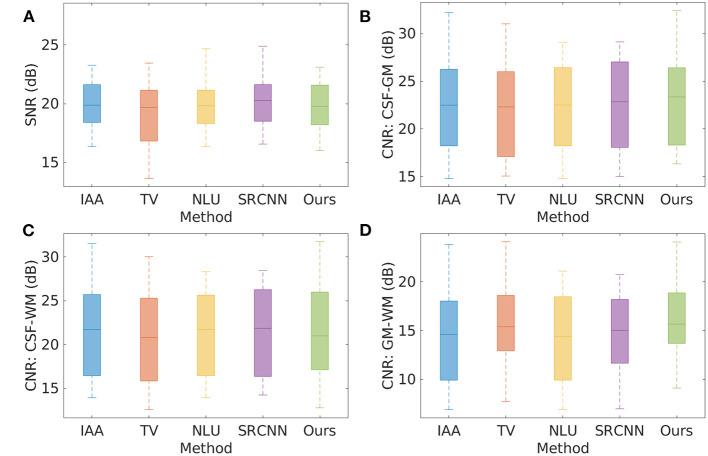
Figure 5.
Quality of the 20 HR images reconstructed by the five SRR methods on the clinical data set in terms of SNR and CNR. (A) SNR; (B) CNR between cerebrospinal fluid and gray matter; (C) CNR between cerebrospinal fluid and white matter; and (D) CNR between gray matter and white matter. The average SNR achieved by the five methods are, respectively: IAA = 20.19 ± 2.57 dB, TV = 19.17 ± 3.40 dB, NLU = 19.92 ± 2.04 dB, SRCNN = 20.18 ± 1.98 dB, Ours = 20.04 ± 2.77 dB. IAA, NLU, and SRCNN generated high SNR, as they benefited from the averaging to improve the SNR and CNR. Our approach offered comparable SNR with IAA, NLU, and SRCNN, and outperformed TV by ~1 dB in terms of SNR. Our approach generated slightly superior CNRs to the five baselines about cerebrospinal fluid, and yielded considerably higher CNR between gray matter and white matter than these baselines.