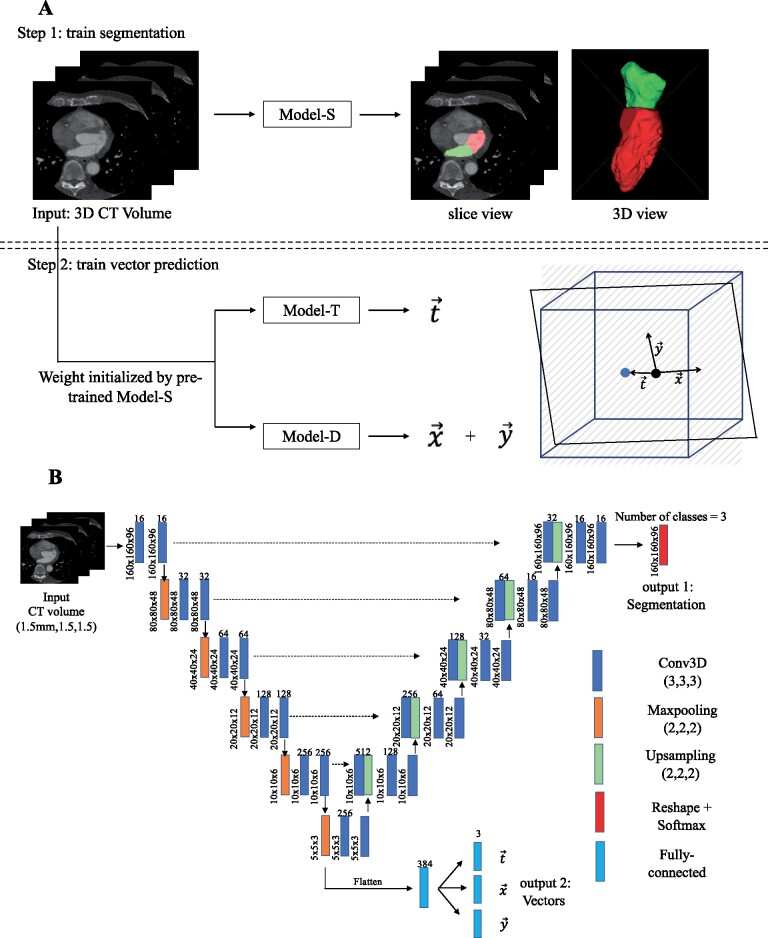
Figure 1.
Deep learning model training approach and model architecture. (A) 3D computed tomography volumes were first resampled to uniform spatial resolution (1.5 mm isotopically) and uniform dimension (160 × 160 × 96) and then served as an input to all models. Step 1: Model-S was trained to predicted LVDL (red) and LADL (green). Step 2: Model-T and Model-D were initialized by Model-S and then trained to predict imaging plane vectors DL, DL, and DL. A graphic illustration of these three vectors in relationship to the image volume is shown. The blue cube represents the computed tomography volume with a re-sliced plane in black. The blue dot is the centre of volume and black dot is the centre of plane. is the displacement between the blue and black dot and and are directional vectors of the 2D plane in the volume’s coordinate system. (B) U-Net architecture with added branch consisting of four fully connected layers after the last max-pooling layer in the down-sampling path was used. Conv3D, 3D convolution layer.