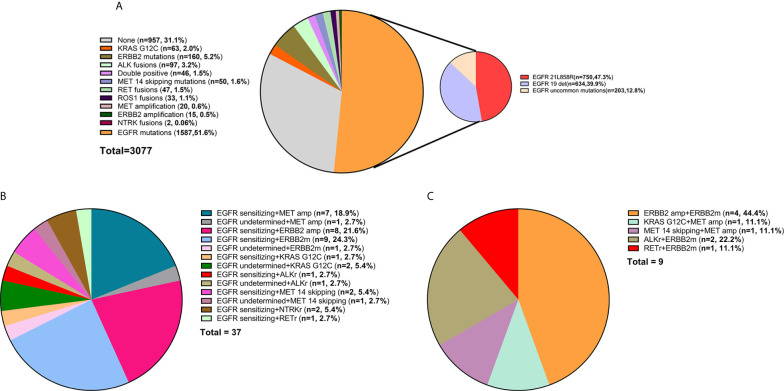
Figure 1.
(A) The frequency of different oncogenic drivers in all patients. (B) Composition of EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients harboring other potentially actionable oncogenic drivers. (C) Composition of NSCLC patients harboring co-occurring potentially actionable drivers without EGFR mutations. Composition of patients with lung adenocarcinoma from MKSCC harboring co-occurring potentially actionable oncogenic drivers. double-positive, with two potentially actionable oncogenic drivers; triple-positive, with three potentially actionable oncogenic drivers; del, deletions; EGFR sensitizing, sensitizing EGFR mutations, EGFR undetermined, undetermined EGFR mutations; amp, amplification; ERBB2m, ERBB2 mutation; MET 14 skipping, MET exon 14 skipping mutation; ALKr, ALK rearrangement; NTRKr, NTRK rearrangement; RETr, RET rearrangement.