FIGURE 2.
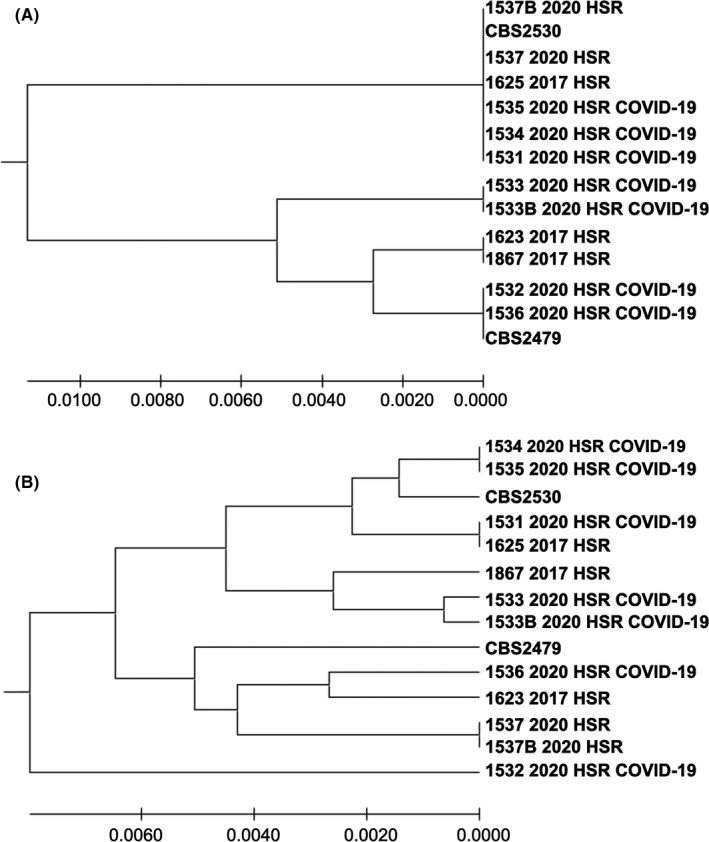
(A) UPGMA phylogenetic tree showing the evolutionary relationship among 14 IGS1 nucleotide sequences, from two reference strains (CBS2479 and CBS2530) and 12 clinical strains from 10 patients from the same hospital. The strains 1533 2020 HSR and 1533B 2020 HSR were recovered from the same patient, as well as the strains 1537 2020 HSR and 1537B 2020 HSR. There were a total of 562 nucleotides positions in the final data set. The final tree with the sum of branch length = 0.0304 is shown. Three strains from different COVID‐19 patients had identical sequences (1531 2020 HSR, 1534 2020 HSR, 1535 2020 HSR); (B) UPGMA phylogenetic tree showing the evolutionary relationship among 14 concatenated (five loci) nucleotide sequences, from two reference strains (CBS2479 and CBS2530) and 12 clinical strains from 10 patients from the same hospital. The strains 1533 2020 HSR and 1533B 2020 HSR were recovered from the same patient, as well as the strains 1537 2020 HSR and 1537B 2020 HSR. There were a total of 2467 nucleotides positions in the final data set. The final tree with the sum of branch length = 0.456 is shown. The strains recovered from the patients hospitalised at the COVID‐19 ICU showed that only two patients had phylogenetic closely related strains (1534 2020 HSR and 1535 2020 HSR strains belong to the same haplotype)
