FIGURE 3.
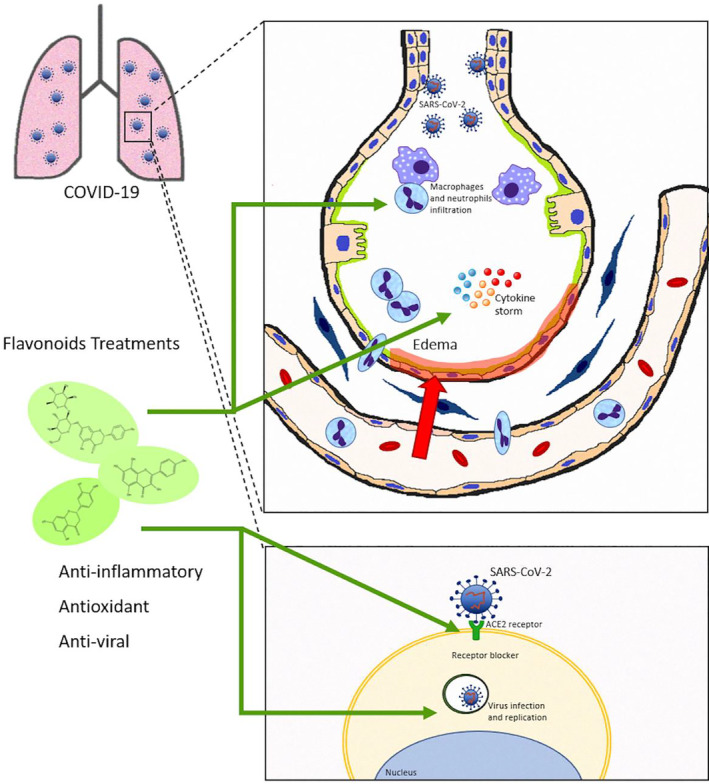
Possible effects of flavonoids on COVID‐19‐induced acute lung injury: COVID‐19 affects several organs, especially the pulmonary system. Severe COVID‐19 is characterized by a cytokine storm and acute lung inflammation that can progress to acute lung injury and systemic inflammation. Acute lung injury is well characterized by endothelium and/or epithelial injury, macrophage activation, neutrophil recruitment, and oxidative stress as well as high cytokine release. The binding of SARS‐CoV‐2 to ACE2 in epithelial cells induces infection and virus replication. The flavonoid has well‐described antiinflammatory, antioxidant, and antiviral effects. The evidence reviewed in the literature shows that flavonoid could be a potential therapeutic target for COVID‐19, since it inhibits the cytokine storm and lung inflammation. In addition, evidence suggests that it can block the entry and replication of the virus, and should be further explored
