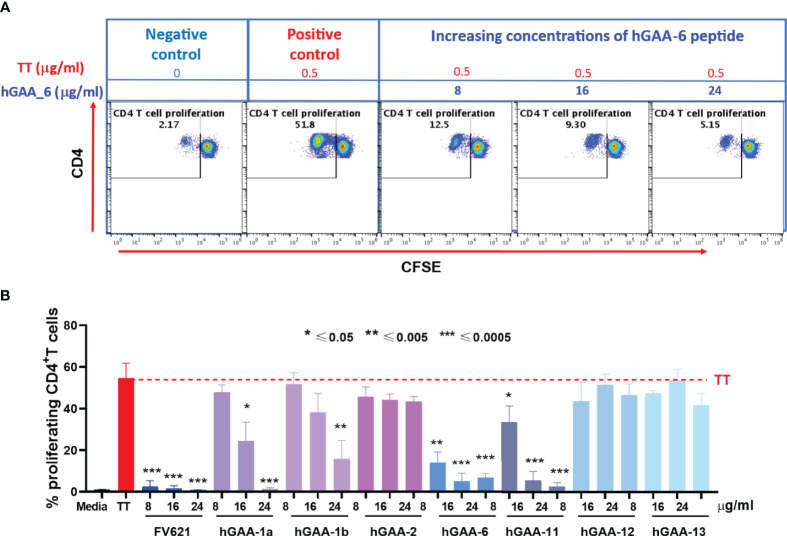
Figure 5.
GAA-derived peptides inhibit memory CD4 T cell response to Tetanus Toxoid (TT) in healthy donors. (A) Representative flow cytometry dot plots show CD4 memory T cell proliferative response to TT and dose-dependent inhibition by hGAA-6 peptide. (B) Inhibition of CD4+T cell recall response by GAA-peptides in TTBSA. PBMCs from healthy donors were stimulated with 0.5 µg/ml of TT with or without FV621 or GAA-peptides and analyzed at six days post-stimulation by flow cytometry for inhibition of CD4+ T cell proliferation. Data are the representative donor from 5 donors in the experiments. Significant suppressive capacity of CD4+ T cell proliferation was observed for 4 putative Treg peptides in GAA confirming their regulatory potential across all donors tested. P values * ≤ 0.05, ** ≤ 0.005 and *** ≤ 0.0005 represents statistical significance between peptide stimulation vs TT using a two-tailed t test. GAA peptides 1a, 1b, 6 and 11 significantly suppressed the expansion of TT-memory T cells in this in vitro assay.