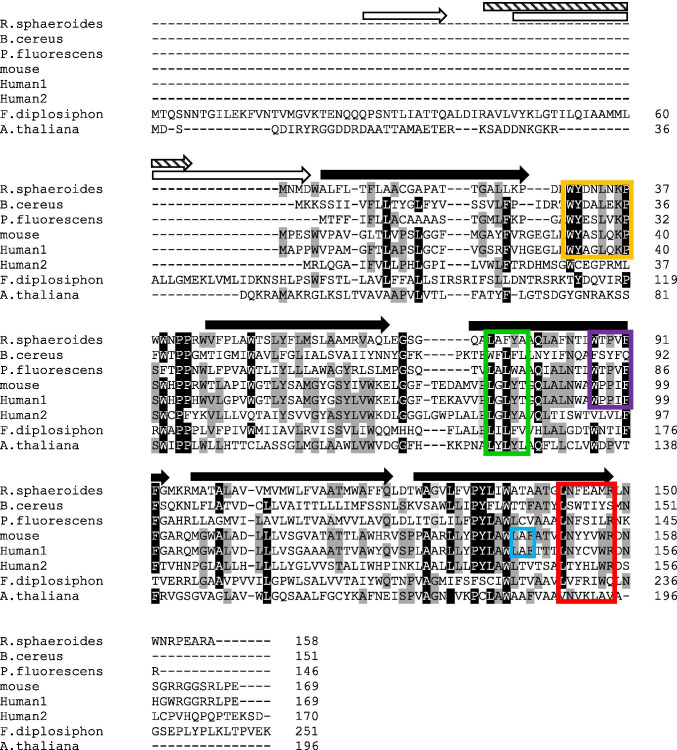
Fig. 1.
Sequence alignment of bacterial, animal, and plant TSPO proteins. Alignment was made with Clustal Omega (Madeira et al. 2019). Black arrows indicate crystallographically-defined transmembrane helices in Rhodobacter sphaeroides TSPO (Li et al. 2016). White arrows indicate additional predicted N-terminal helices of Arabidopsis thaliana TSPO (Jurkiewicz et al. 2020). The striped arrow indicates an additional predicted N-terminal helix in Fremyella diplosiphon TSPO1 (Busch et al. 2017). The LAF and CRAC motifs are outlined in blue and red, respectively. The AIM motif (Hachez et al. 2014) is outlined in green, the 14-3-3 binding motif (Aghazadeh et al. 2012) is outlined in yellow and the WxPxF motif (Li et al. 2016) is outlined in purple. Amino acids that are 80–100% identical are shown in black with white letters; those that are 50–70% identical are shown in gray