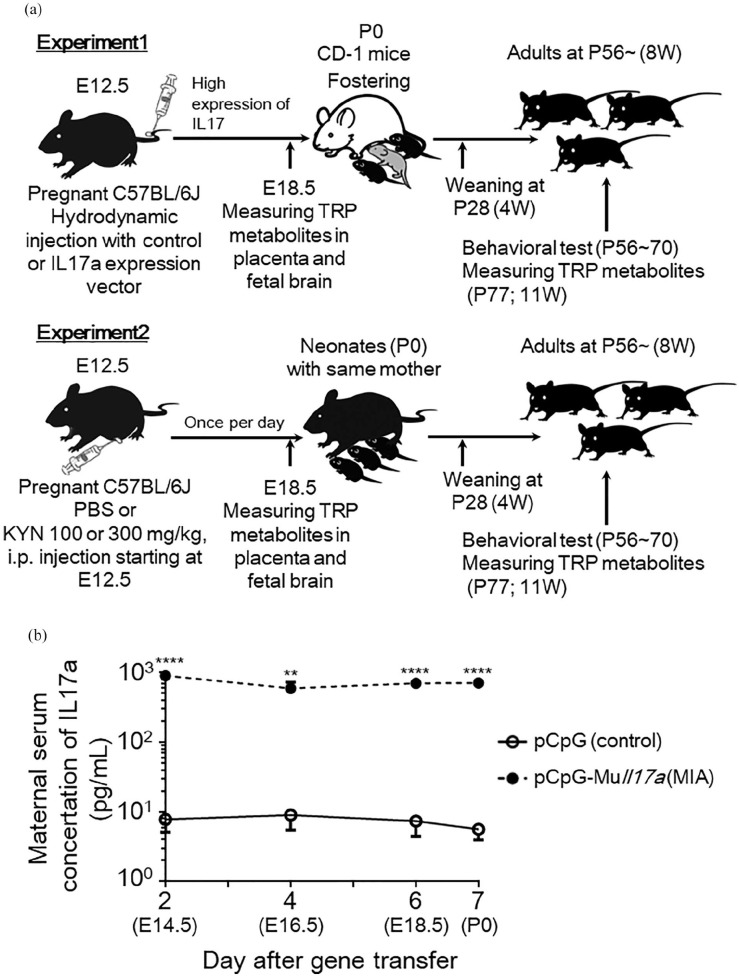
Figure 1.
Experimental design of maternal immune activation (MIA) and kynurenine administration. (a) Experiment 1: dams were injected with pGpG-mcs (control vector) or pCpG-Muil17a (IL-17A-expressing vector) on embryonic day 12.5 (E12.5) at a dose of 0.1 pmol/mouse. CD-1 mice were used as fostering mothers on postnatal day 0 (P0) until weaning of pups on P28 for both control and MIA mice. Experiment 2: dams were injected intraperitoneally with vehicle (5%NaOH + phosphate-buffered saline; PBS) or kynurenine (KYN) at a dose of 100 or 300 mg/kg body weight/day from E12.5 until E19.0. All pups remained with the same dams until weaning on P28. For both experiments, maternal serum, placenta, fetal-pooled plasma and brain regions were acquired at E18.5 for the measurement of tryptophan (TRP) metabolites. Behavioral tests were performed in adult animals between P56 and P70. All animals were euthanized on P77 for measurement of TRP metabolites in adult brain region. (b) Serum concentrations of maternal IL-17A (N = 3-4 mice per group, 3 independent experiments) at E14.5 until birth (E19.5) in pCpG-mcs- or pCpG-Muil17a-injected mothers. Data are represented as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Student’s t-test, **P < .01, ****P < .0001 versus control (pCpG-mcs-injected mice).