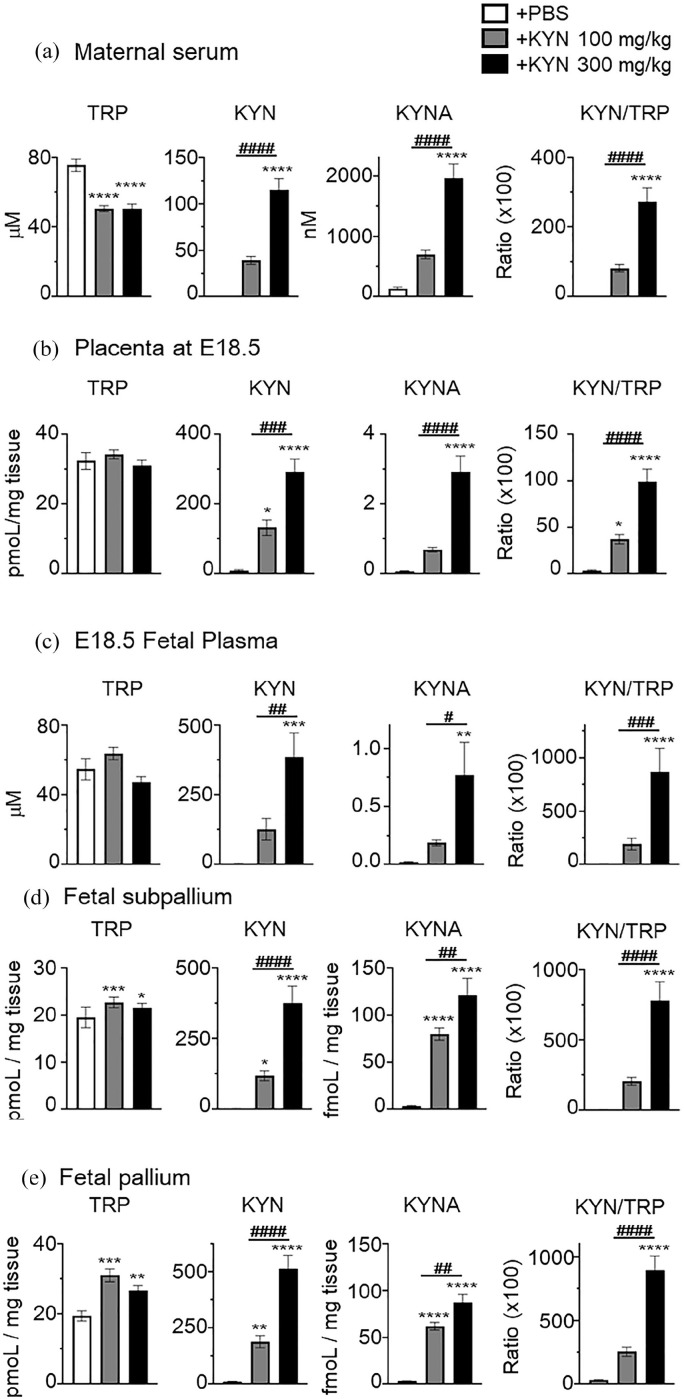
Figure 4.
Low or high dose of kynurenine (KYN) administration significantly increased the levels of tryptophan (TRP) metabolites in maternal serum, placenta, fetal plasma and brain. We measured TRP metabolites 90 minutes after final intraperitoneal injection in pregnant mice on embryonic day 18.5 (E18.5) with either PBS (vehicle), low (100 mg/kg), or high (300 mg/kg) dose of kynurenine (KYN). The concentrations of TRP, KYN, kynurenic acid (KYNA) and the ratio of KYN/TRP in maternal serum (a) (N = 6-8), placenta (b) (N = 11-16, 3 independent experiments), fetal plasma (c) (N = 4-5 pooled plasma per group), and fetal brain region of subpallium (d) and pallium (e) (N = 22-30, 3 independent experiments). Data are presented as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test, *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001, versus + PBS mice, #P < .05, ##P < .01, ###P < .001, ####P < .0001, versus + KYN 100 mg/kg mice.