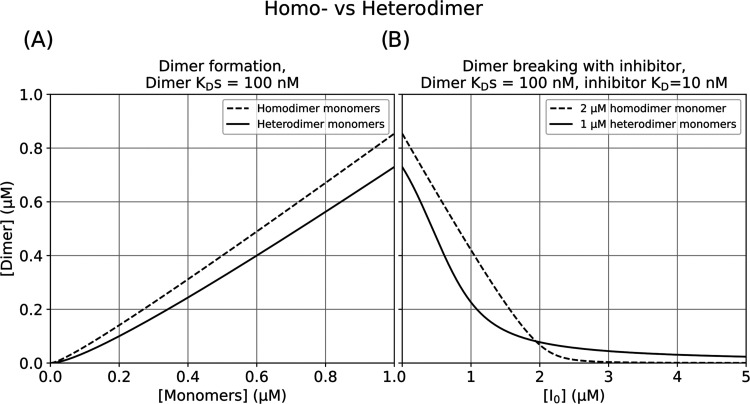
Figure 1.
Homo-vs-Heterodimer making and breaking. (A) Dimer formation with a KD of 100 nM as a function of monomer concentration. As a homodimer (broken line) contains two copies of the same monomer, the total monomer concentration is twice that shown on the x-axis. Heterodimer formation (solid line) contains two different monomers with the concentration for each monomer given by the x-axis. (B) After monomer titration to 1 μM as shown in (A), or effectively 2 μM in the homodimer case, the resultant complex has an inhibitor (I0) titrated against it. The inhibitor has a KD of 10 nM to one heterodimer monomer (solid line) and the same KD to homodimer monomers.