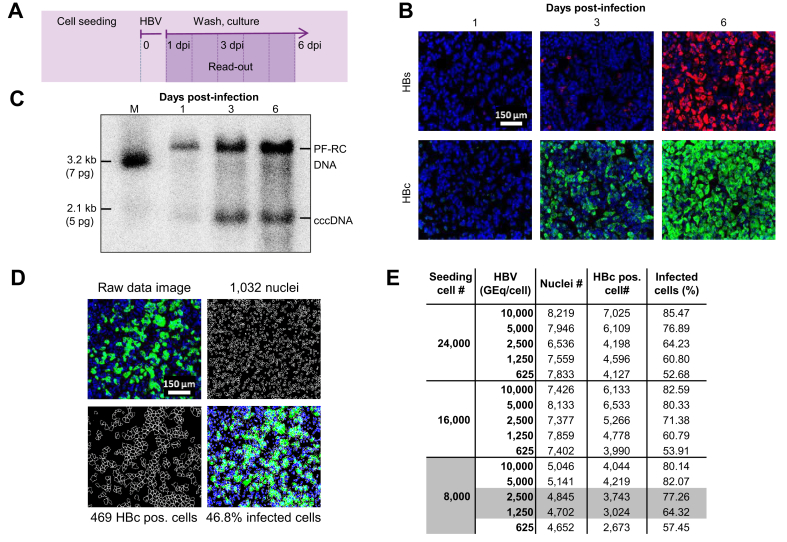
Fig. 1.
Development of a phenotypic HBV infection assay.
(A) Schematic illustration of the assay. Time-dependent analysis of HBV infection using (B) IFA of intracellular HBc and HBs expression and (C) cccDNA formation by Southern blotting at 1, 3, and 6 dpi of HepG2-NTCPsec+ cells. (D) Microscopic image processing and analysis for quantification of HBV-infected cells. Representative raw data images (top left), counting of individual nuclei (top right with 1,032 nuclei), and individual HBc-positive cells (lower left with 469 HBc-positive single cells). Absolute counts were used to determine relative values of ~47% of infected cells (lower right). (E) Assessment of cell density and HBV GEq/cell for phenotypic analysis of HBV infection. HepG2-NTCPsec+ cells were seeded at 8,000, 16,000, or 24,000 cells/well in 384-well plates and inoculated with 313–10,000 HBV GEq/cell. Cells were fixed at 6 dpi, and the number of nuclei, HBc-positive cells, and relative percent of infected cells were determined as described (D). A total of 6 individual pictures/well (in duplicate) were used for calculations. Nuclei (blue), HBs (red), and HBc (green). cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; dpi, days post-infection; GEq, genome equivalents; IFA, immunofluorescence analysis.