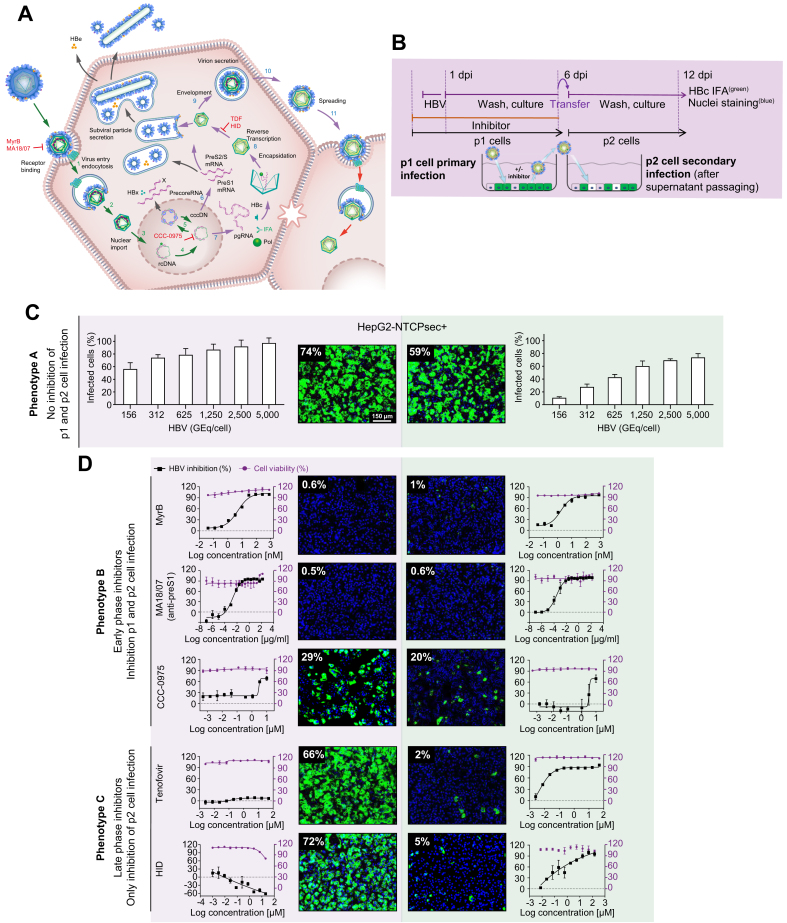
Fig. 2.
Establishment of an HBV infection assay to monitor the entire HBV life cycle.
(A) HBV life cycle scheme. Early life cycle steps of infection establishment (1–5, green arrows) inhibited by reference inhibitors MyrB, MA18/07 (Step 1, receptor binding), and CCC-0975 (Step 5, cccDNA formation). Late HBV life cycle steps of morphogenesis and egress (6–12, blue arrows) inhibited by TDF and HID (Step 9, reverse transcription, RNase H). (B) Experimental setup of the 2-step HBV supernatant transfer infection assay. HepG2-NTCPsec+ p1 cells were seeded at 8,000 cells/well in 384-well plates and pre-incubated with the early or late life cycle phase reference inhibitor MyrB, MA18/07, CCC-0975, TDF, or HID for 2 h prior to inoculation with HBV for 18 h. After cells had been repeatedly washed at 1 dpi, they were treated with reference inhibitors and cultured until 6 dpi. Supernatants were harvested and transferred to naïve HepG2-NTCPsec+ p2 cells. Cells p1 and p2 were analysed using IFA (HBc) and counterstained with Hoechst (nuclei). Infected cells were identified microscopically and analysed as described in Fig. 1. (C) Infection with serially diluted HBV under untreated conditions (phenotype A). (D) HBV infection under treatment with early HBV life cycle inhibitor (phenotype B, top panel) or late HBV life cycle inhibitor (phenotype C, lower panel). HBc (green) and nuclei (blue); dose-response curve regression: red line = % cell viability (right y-axis); black line = % inhibition of infection (left y-axis). cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; dpi, days post-infection; HID, N-hydroxyisoquinolinedione; IFA, immunofluorescence analysis; MyrB, myrcludex B; pgRNA, pregenomic RNA; TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.