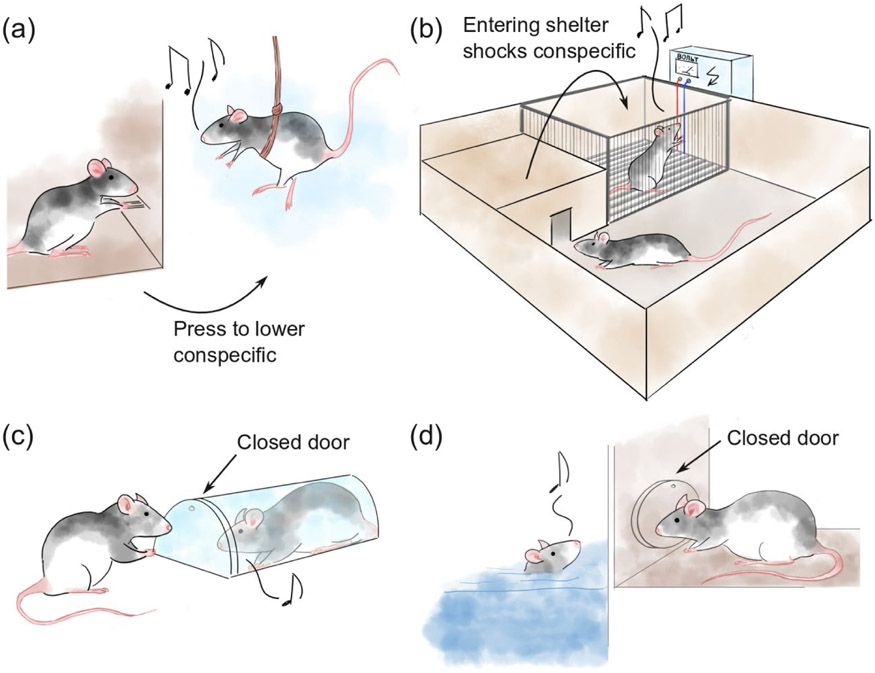
Figure 3: Investigating body language signals of distress.
(a) A classic paradigm to investigate actibe helping in rats: Aversive dangling from a harness. (Rice and Gainer, 1962) (b) Another classic paradigm: One rat has to decide between a brightly lit arena and a dark and comforting shelter. Entering the shelter delivers a shock to a nearby conspecific. (Preobrazhenskaya and Simonov, 1974). (c) The aversive-restraint-tube paradigm: One rat can open a door that lets a conspecific escape a transparent tube. (Bartal et al., 2011) (d) The aversive-swimming-pool paradigm: One rat can open a door that lets a conspecific escape a pool of water. (Sato et al., 2015).