FIGURE 2.
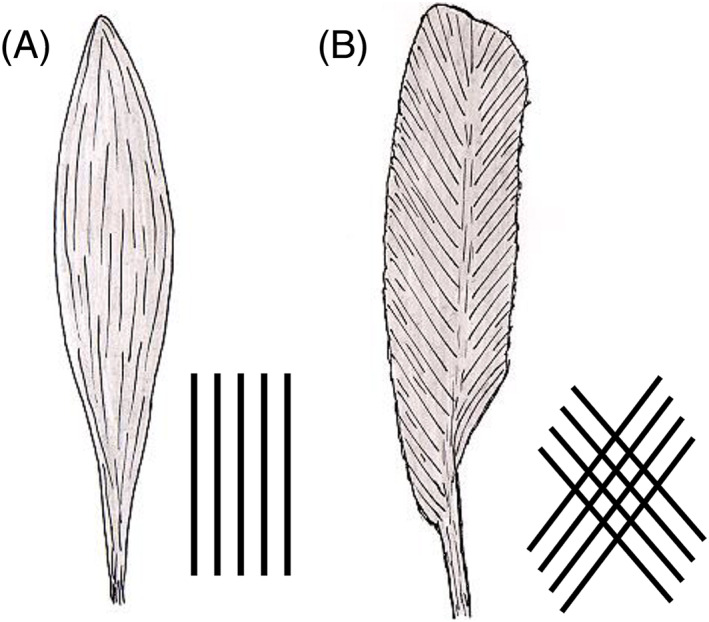
Typical shapes of skeletal muscle. In spindle‐shaped (fusiform) muscles (A; left), for example the tibialis anterior, fibers are oriented nearly parallel along the axis of the muscle. In feathered (pennate) muscles (B; right) such as the soleus muscle in the calf, fibers are arranged in a crossing pattern and the orientation of the fatty septa shows a distinct angle with respect to the orientation of the tendons
