FIGURE 3.
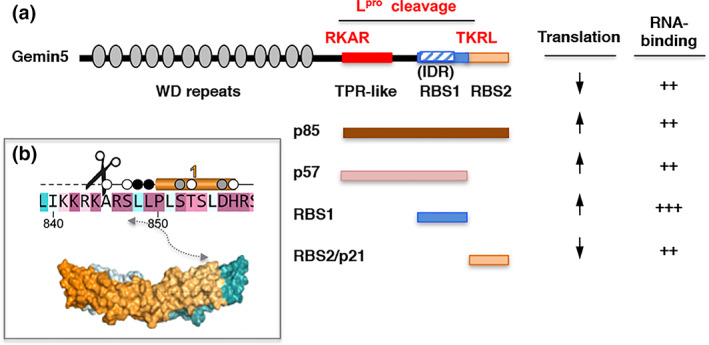
Outline of Gemin5 functional domains. (a) Diagram of the Lpro cleavage sites in Gemin5 protein. The structural domains of Gemin5 (170 kDa) are represented at the top. The WD repeats located at the N‐terminus are involved in snRNPs assembly and ribosome interaction. The TPR‐like domain in the central region mediates dimerization of the protein. The non‐canonical RNA binding site (RBS1) located at the C‐terminus harbors an IDR, and contributes to selective translation control counteracting the negative effect of Gemin5 in global translation. In contrast, the unstable RBS2/p21 moiety downregulates IRES‐dependent translation. The products p85 and p57 resulting from the sequential Lpro cleavage at the RKAR and TKRL sites are depicted. the role of the protein fragments in translation upregulation or downregulation, and RNA‐binding capacity is indicated. (b) Structural features of the RKAR motif. Residues are colored according to the conservation, from magenta (identity) to cyan (variable). The scissors mark the Lpro cleavage motif. The helix 1 is depicted above the sequence. Residues buried up to 40%, 80%, or 100% in the dimerization interface are denoted with a white, gray or black dot. The approximate position of the RKAR motif on the three‐dimensional structure of the TPR‐like dimer is depicted by a double arrow
