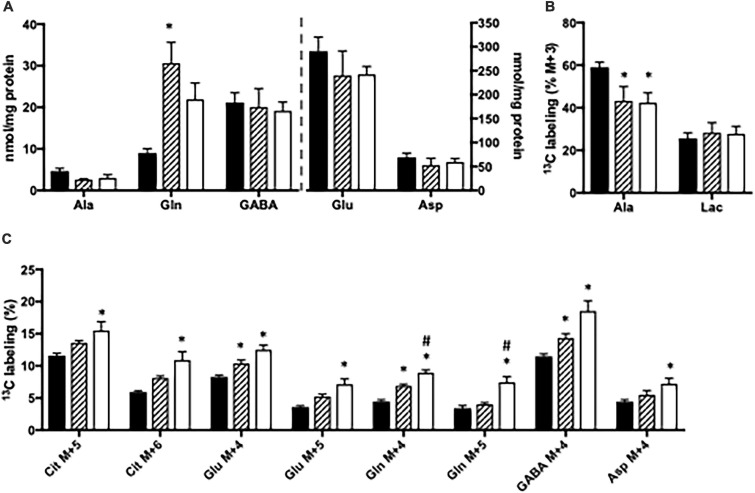
FIGURE 4.
Hippocampal slices from CNS-Glud1–/– mice were incubated in medium containing 5 mM [U-13C]glucose and 0 mM (control; filled bars), 1 mM (hatched bars), or 5 mM (open bars) NH4Cl. The effect of ammonia treatment on the amounts (nmol/mg protein) of alanine, glutamine, GABA, glutamate, and aspartate (A) and the percent 13C labeling originating from [U-13C]glucose in alanine M + 3 and lactate M + 3 (B) and in citrate M + 5, citrate M + 6, glutamate M + 4, glutamate M + 5, glutamine M + 4, glutamine M + 5, GABA M + 4, and aspartate M + 4 (C). The hippocampal slices from CNS-Glud1–/– mice were incubated in the presence of [U-13C]glucose for 60 min as detailed in Materials and methods. The amounts of metabolites were determined employing HPLC while the percent enrichment was determined from GC-MS analysis of slice extracts as detailed in Materials and methods. Results are averages ± SEM (n = 6–10), and the asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference from hippocampal slices from CNS-Glud1–/– mice incubated in the absence and presence of 1 or 5 mM NH4Cl while a number sign indicates a statistically significant difference between hippocampal slices from CNS-Glud1–/– mice incubated in 1 and 5 mM NH4Cl (P < 0.05). Ala, Alanine; Lac, Lactate; Cit, Citrate; Glu, Glutamate; Gln, Glutamine; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; Asp, Aspartate.