Figure 3.
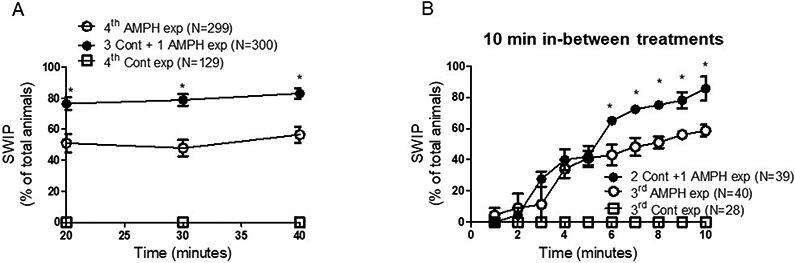
Tolerance to amphetamine is maintained over 40-minute treatments and with reduced intervals between exposures. A, animals were exposed to control (open squares), AMPH (open circles) or control followed by AMPH (filled circles) as described in Figure 2A. But, during the last exposure, the percentage of animals exhibiting SWIP was measured up to 40 minutes. The percentage of animals exhibiting SWIP in the group that received four AMPH exposures was statistically lower than the animals that received three control and one AMPH exposure throughout the 40-minute observation (*p < 0.001, 2-way ANOVA test). B, animals were exposed three times to control- (open squares) or AMPH-solution (open circles) and two times to control followed by one time to AMPH (filled circles). Between each exposure, animals were allowed to recover and feed in drug-free agar plates for 10 minutes. Statistical difference between animals that received three AMPH exposures and animals that received two control- followed by one AMPH-exposure was achieved after six minutes of the last exposure (*p < 0.05, 2-way ANOVA test). N represents the number of animals tested per each group.
