Figure 1.
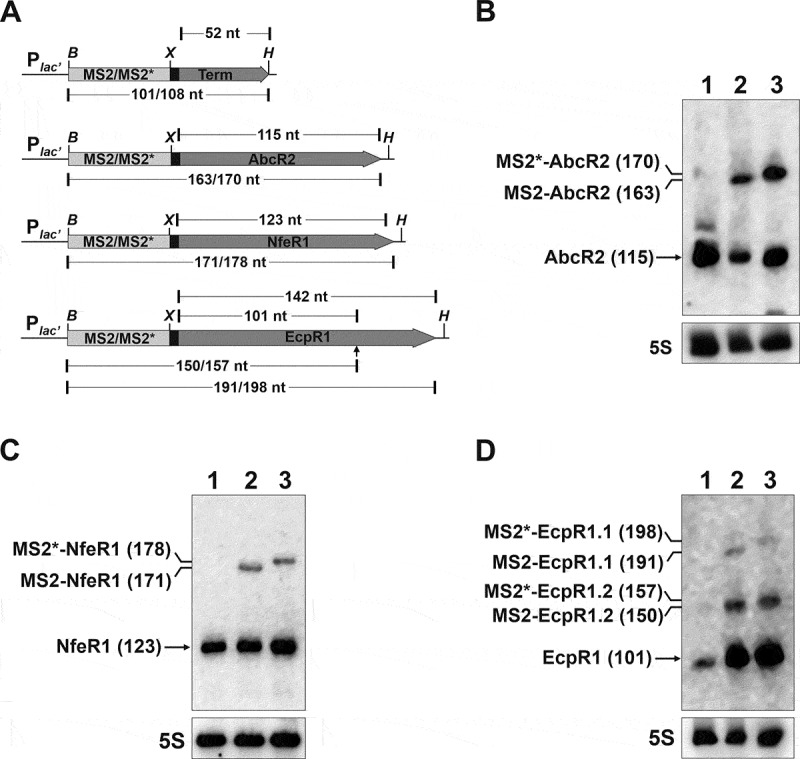
Expression of aptamer-tagged trans-sRNAs in S. meliloti. (A) Schematics (drawn to scale) of the genetic constructs to express the MS2/MS2*-tagged AbcR2, NfeR1 and EcpR1 sRNAs, and the Term control from an engineered constitutive Plac’ promoter. The expected length (nt) of the RNA species derived from each construct is indicated. The arrowhead indicates the processing site of the full-length EcpR1 wild-type transcript. Sites used for cloning were BamHI (B), XbaI (X) and HindIII. (B, C, and D) Northern blot detection of aptamer-tagged sRNAs. Total RNA from strain SmhfqFLAG transformed with either pSRK-MS2-Term, pSRKMS2/MS2*-AbcR2, pSRKMS2/MS2*-NfeR1 or pSRKMS2/MS2*-EcpR1, was probed with specific oligonucleotides targeting AbcR2 (A), NfeR1 (B) and EcpR1 (C), respectively. The detected RNA species and their length (nt) are indicated to the left of each panel. 5S rRNA was probed as RNA loading control. Lanes: 1, MS2-Term-expressing cells; 2, bacteria expressing the corresponding MS2-tagged sRNA; 3, bacteria expressing MS2*-tagged sRNA. Expression of wild-type endogenous sRNAs was induced by growth of bacteria in MM to log phase (NfeR1) or by an osmotic upshift (AbcR2 and EcpR1)
