Figure 2. Similar magnitude and kinetics of NK direct poly-functionality despite heightened NK activation in PWID compared to control donors.
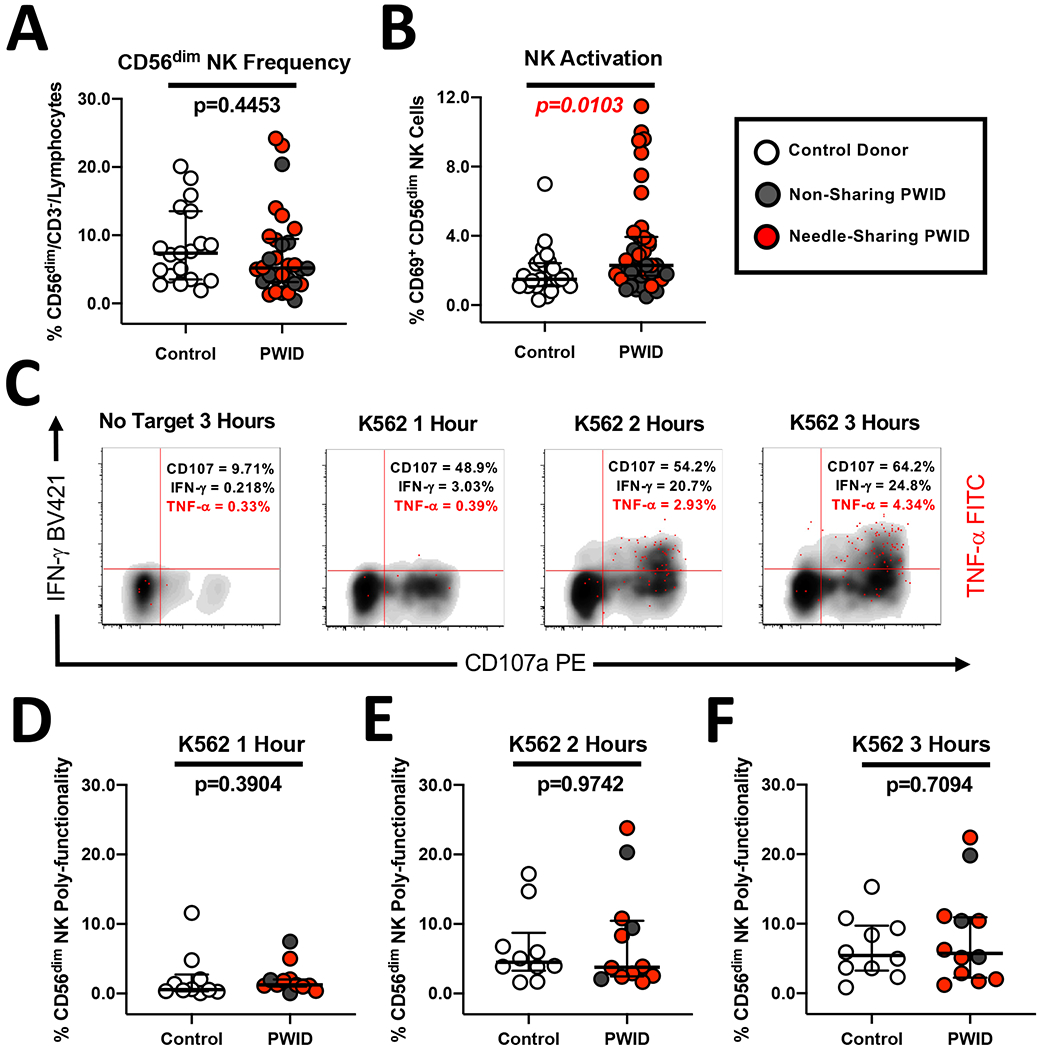
(A) Composite graph displaying the similar frequency of CD56dim/CD3− NK cells from non-sharing (light gray circles) and needle-sharing (dark gray circles) PWID compared to control donors (white circles). (B) Composite graph displaying the increased constitutive CD69 activation of CD56dim/CD3− NK cells from PWID compared to control uninfected donors. (C) Representative kinetic analysis of the NK poly-functional profile against K562 tumor targets recognized through the direct cytotoxicity pathway. PBMCs from a representative PWID were incubated for 3 hours in the presence or absence of MHC-devoid K562 cells at a 5:1 effector to target cell ratio. PBMCs were then stained with fluorescently conjugated antibodies to NK phenotypic markers and permeabilized to measure intra-cellular cytokine expression. The data is shown in a three-parameter poly-functional density plot with CD107a degranulating NK cells on the X-axis, IFN-gamma producing NK cells on the Y-axis, and NK cells producing TNF-alpha super-imposed on top as red dots. The percentage of CD56dim/CD3− gated NK cells staining positive for CD107a, IFN-gamma, and TNF-alpha is shown in the upper right-hand quadrant. (D-F) Composite graph of K562-induced NK poly-functionality from PWID and control donors was defined as the percentage of CD56dim/CD3− gated NK cells exhibiting two or more effector functions including degranulation and/or cytokine production at each timepoint after subtraction of background from the No Target control condition. Statistical analyses of two groups was performed using a non-parametric Mann-Whitney T-test with a two-tailed p-value.
