Figure 3. GRs regulate FKBP5 expression under Dex-stimulated, but not under baseline, conditions in mouse primary hippocampal neurons.
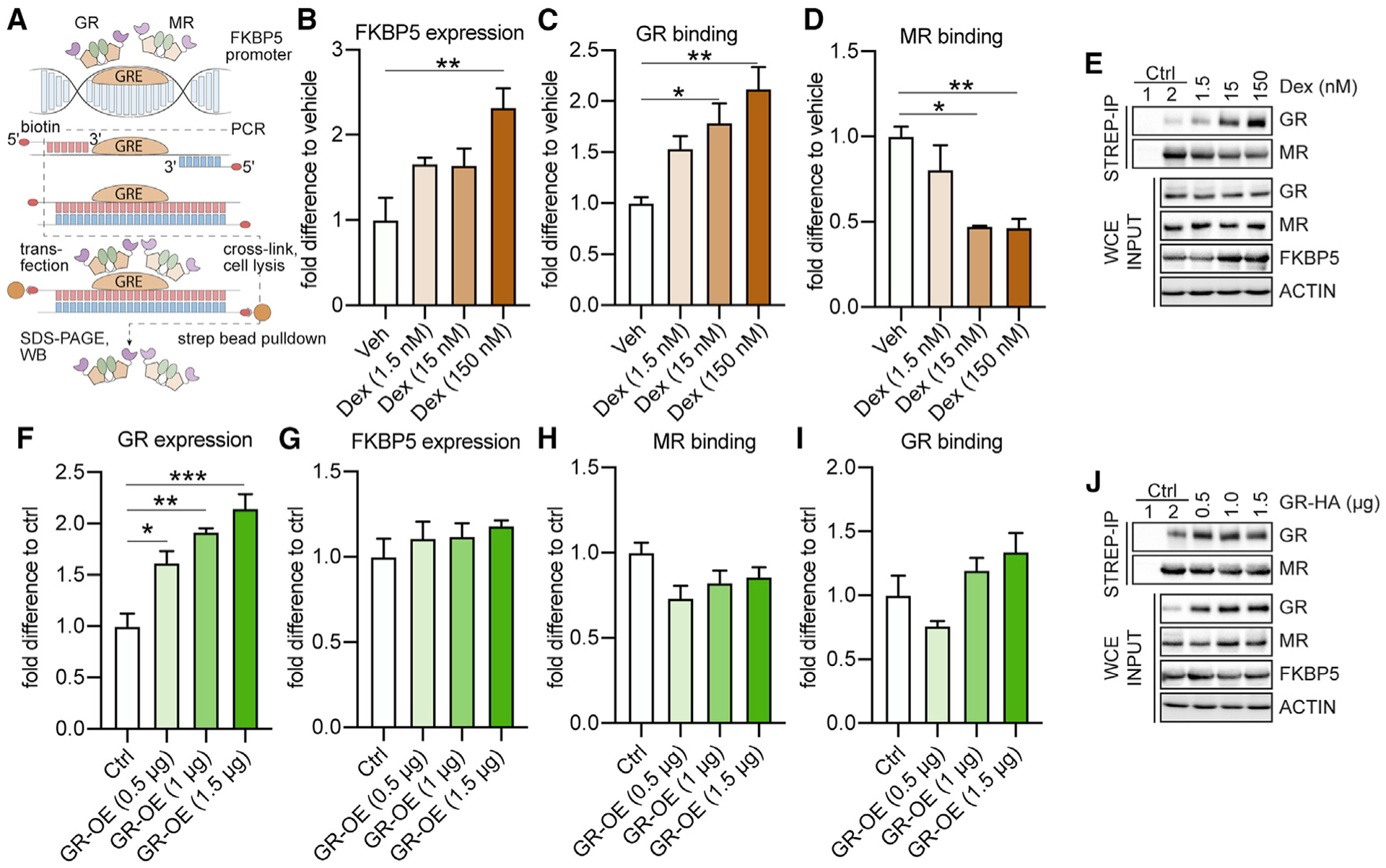
The effects of altered GR levels on FKBP5 expression and on MR and GR binding to two Fkbp5-glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) were examined under baseline conditions and following dexamethasone (Dex) stimulation in primary hippocampal neurons, using biotinylated oligonucleotide immunoprecipitation (oligoIP).
(A) Schematic summary of the experimental setup. After oligoIP, MR and GR binding to the Fkbp5-GRE oligonucleotide were quantified by western blotting using antibodies specific for the respective receptor. In addition, FKBP5, MR, or GR expression levels were quantified by western blotting from whole-cell extracts (WCEs).
(B) Dex treatment increased FKBP5 levels in a concentration-dependent manner (F3,8 = 7.278, p < 0.05).
(C and D) GR binding to the Fkbp5-GRE oligonucleotide was increased following Dex treatment (F3,8 = 8.9, p < 0.01), while MR binding was decreased (F3,8 = 10.35, p < 0.01).
(E) Example blots of (B)–(D). Ctrl (control) 1: magnetic beads lacking conjugated streptavidin. Ctrl 2: cells treated with vehicle (Veh).
(F) Transfection with a GR-expressing plasmid concentration dependently increased GR protein expression (F3,8 = 19.25, p < 0.001).
(G–I) FKBP5 expression and MR and GR binding to the Fkbp5-GRE oligonucleotide are not altered following GR overexpression (OE) under baseline conditions.
(J) Example blots of (F)–(I). Ctrl 1: magnetic beads lacking conjugated streptavidin. Ctrl 2: cells transfected with empty Ctrl vector.
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) + Bonferroni post hoc test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as mean + SEM (n = mean derived from three independent experiments).
