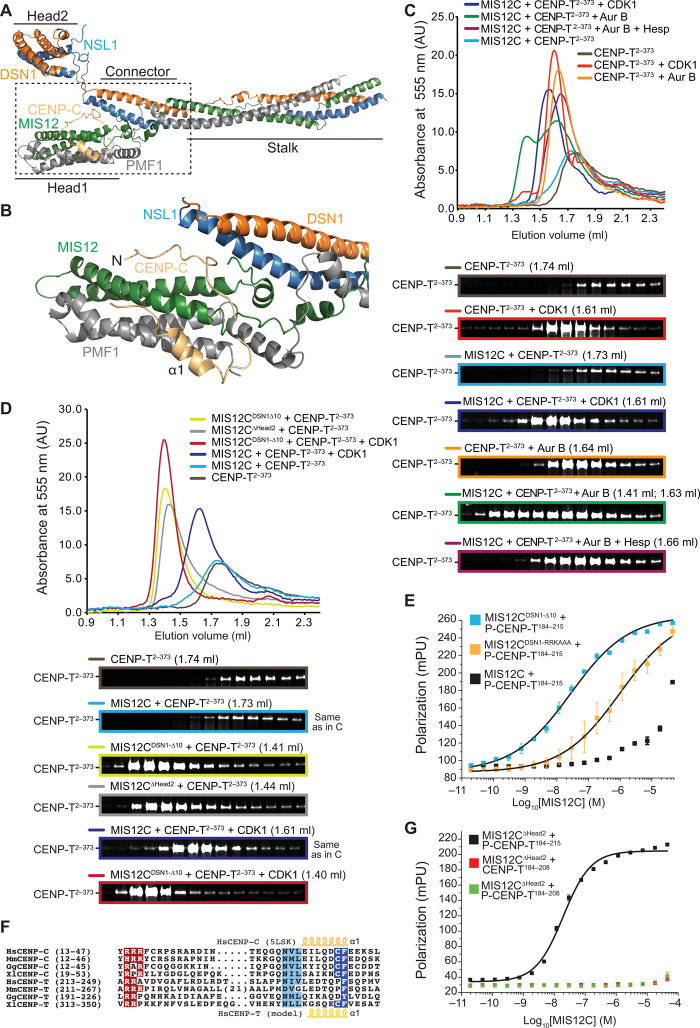
Fig. 6. Molecular mechanism of the CENP-T:MIS12C interaction.
(A) Cartoon model of the human MIS12 complex in complex with the CENP-C N-terminal region [Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID 5LSK]. (B) Close-up of the MIS12C:CENP-C interaction interface. (C) SEC on a Superdex 200 column of the indicated species with the peak elution volume and resulting SDS-PAGE. (D) SEC on a Superdex 200 column of the indicated species with the peak elution volume and resulting SDS-PAGE. Note that the elution profiles and SDS-PAGE for the MIS12C + CENP-T sample (light blue) and for the MIS12C + CENP-T + CDK1 (dark blue) are the same as those displayed in (C) and are only displayed here for easier comparison. (E) Binding isotherms by fluorescence polarization with a fluorescent Ser201-phosphorylated CENP-T184–215 peptide and the indicated MIS12 complex variants. (F) Multiple sequence alignment of segments of the MIS12 complex binding regions of CENP-C and CENP-T from the indicated species. Hs, H. sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus; Gg, Gallus gallus; Xl, Xenopus laevis. (G) Binding isotherms by fluorescence polarization obtained with the indicated fluorescent S201-phosphorylated or nonphosphorylated CENP-T peptides and the MIS12∆Head2 mutant complex. mpu, millipolarization unit.