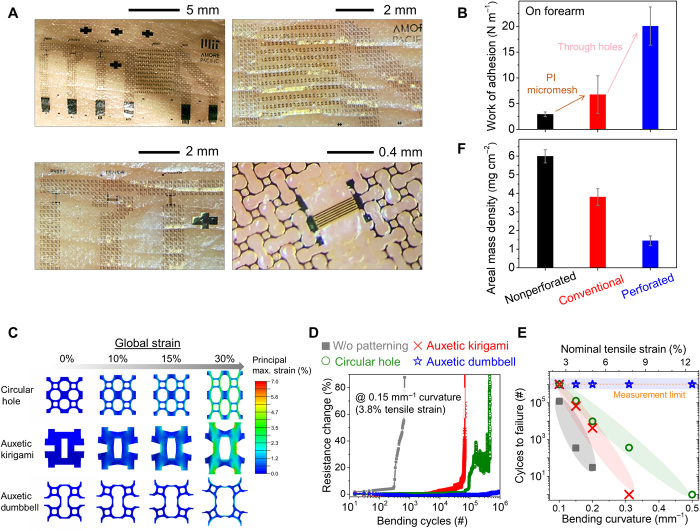
Fig. 3. Mechanical performance of perforated e-skins.
(A) Optical images of perforated e-skins showing conformal contact on the forearm. (B) Work of adhesion of nonperforated, conventional, and perforated e-skins. (C) Strain distribution of three different patterns (circular hole, auxetic kirigami, and auxetic dumbbell) in uniaxial stretching simulation. (D) Cyclic bending fatigue test of e-skins under 0.15 mm−1 bending curvature (3.8% nominal tensile strain) with various perforated patterns (no-pattern, circular hole, auxetic kirigami, and auxetic dumbbell holes). (E) Mechanical durability of e-skins with respect to the bending curvature. (F) Areal mass density of e-skins.