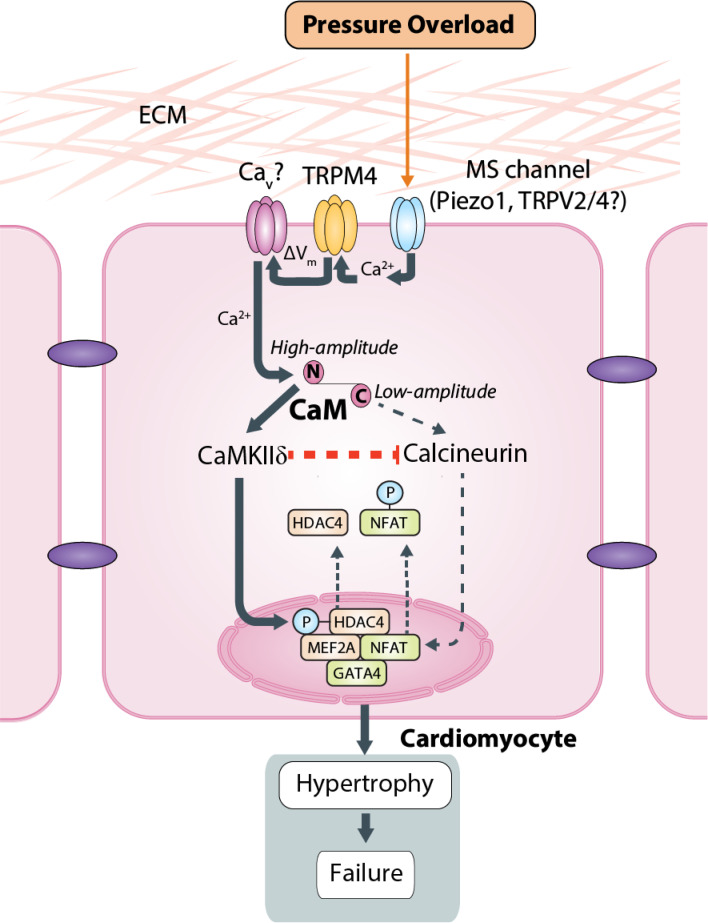
Figure 6. Schematic of the putative TAC-induced pathway that culminates in left ventricular hypertrophy.
A Ca2+-permeable MS channel (e.g. Piezo1, TRPV2, TRPV4) acts as the mechanotransducer providing local Ca2+ that in turn stimulates TRPM4. The Na+-permeable TRPM4 activity then could either stimulate voltage-gated Ca2+ channels through membrane depolarisation or induce reverse activity of the Na+/ Ca2+exchanger through local Na+ loading. Either of these outcomes would lead to a high-amplitude increase in local Ca2+. Calmodulin then responds to this high-amplitude Ca2+ stimulus through the lower affinity Ca2+ binding site at its N-lobe which subsequently activates CaMKIIδ and thus stimulates the CaMKII-HDAC4-MEF2 pathway as shown in Yu et al., 2021. Calcineurin activation is inhibited by the activated CaMKIIδ and is activated preferentially by low-amplitude Ca2+ signalling via Gq-coupled receptors and calmodulin (see Discussion). ECM: extracellular matrix, MS: mechanosensitive, Cav: voltage-gated Ca2+ channel, ΔVm: membrane depolarisation, CaM: calmodulin.