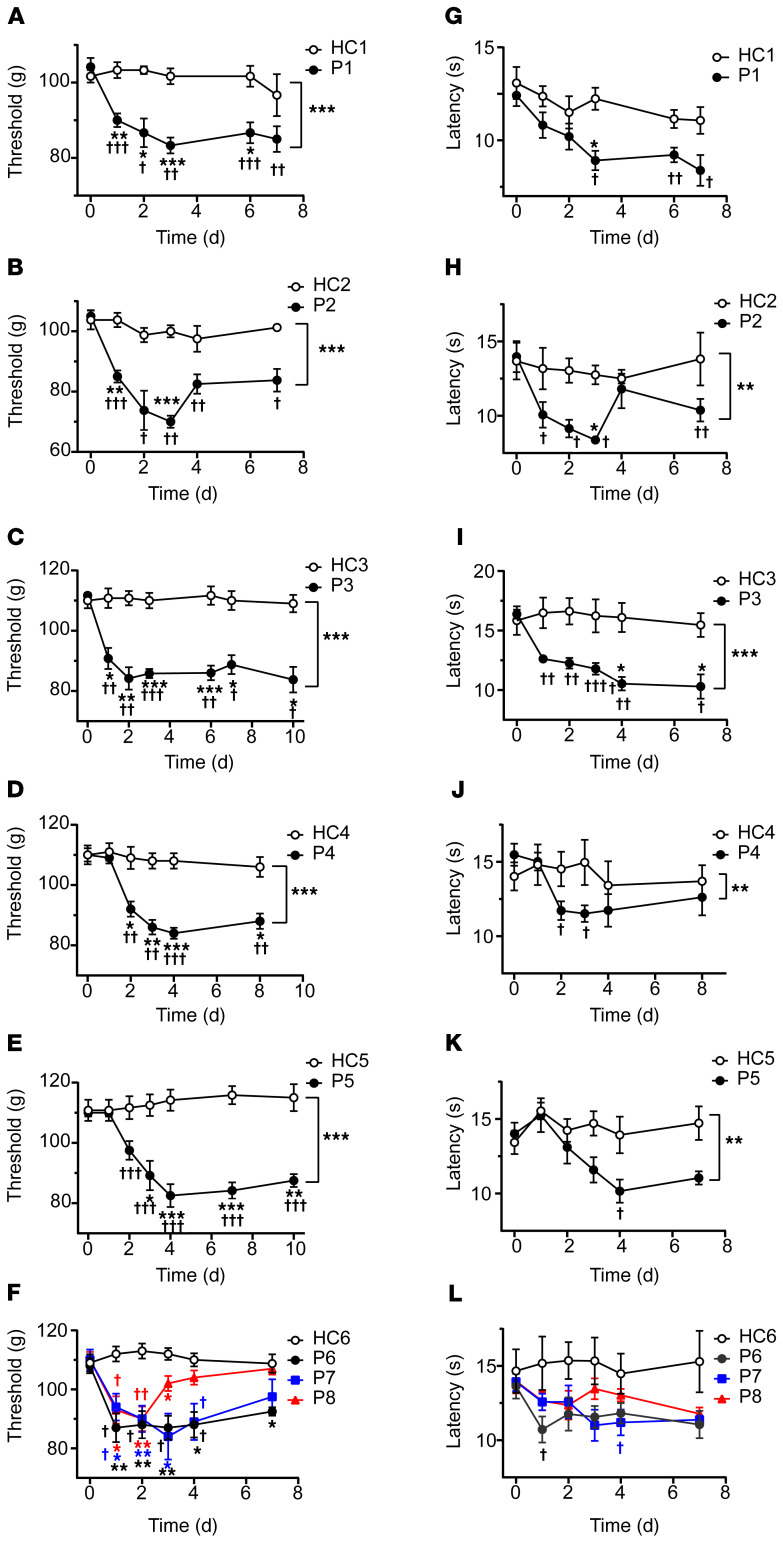
Figure 1. Passive transfer of hypersensitivities from fibromyalgia patients to mice.
Administration of IgG (8 mg on 4 consecutive days) from each of 8 different FMS patients (P1–P8) significantly reduced the withdrawal threshold in the paw-pressure test (A–F) compared with IgG from healthy control subjects (HC1–HC6). The paw withdrawal latency in the cold-plate test was reduced by IgG from 7 of 8 patients (G–L). Data points are mean ± SEM of n = 6 mice in A, C, E, G, I, and K; n = 5 in D, F, J, and L; and n = 4 in B and H. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, FMS IgG compared with HC IgG; 2-way repeated measure ANOVA followed by Sidak’s correction. †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01, †††P < 0.001, compared with the naive preinjection value at time zero; 2-way repeated measure ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test.