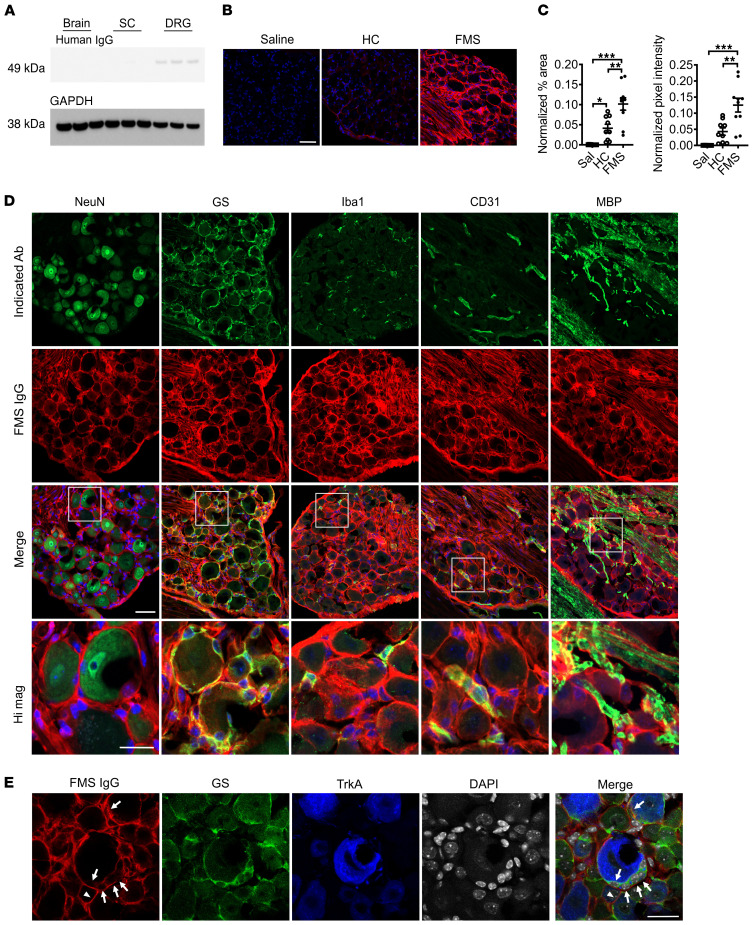
Figure 7. FMS IgG accumulates in the DRG and binds satellite glial cells.
Following IgG injection into mice, Western blot analysis detected FMS IgG in the DRG but little to no IgG in spinal cords (SC) or brains (A) (pooled IgG, 8 mg per day for 4 consecutive days, tissue collected after last injection). FMS IgG, but not HC IgG, accumulates in the DRG 14 days after the first IgG injection (B and C). Human IgG is red and DAPI is blue. Human IgG immunoreactivity in the neuron-rich area was quantified by assessing the percentage area that was immunoreactive for human IgG and the mean pixel intensity of human IgG. Percentage area and pixel intensity were normalized to the DAPI signal (n = 9–10; data points are median ± 95% CI). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. FMS IgG immunoreactivity does not colocalize with neuronal NeuN staining but does colocalize with satellite glial cells (SGCs) (glutamate synthase–expressing [GS-expressing] cells), some macrophages (Iba1-expressing cells) and blood vessels (CD31-expressing cells), and myelinated fiber tracts (myelin basic protein [MBP] staining), but not to myelinated fibers in the DRG (D). To further delineate between SGCs and neuronal membranes, FMS IgG immunoreactivity colocalization was compared with GS and TrkA (a membrane receptor expressed by a subset of nociceptors). FMS IgG colocalizes with GS-expressing SGCs (white arrows) but may also infrequently bind to TrkA-positive neuronal cell membranes (white triangles) (E). Scale bars indicate 50 μm, except the high-magnification image scale bar and scale bar in E, which indicate 25 μm.