Figure 1 |. BRCA1 interacts with Dicer and Ago1/2 to prevent R-loop damage.
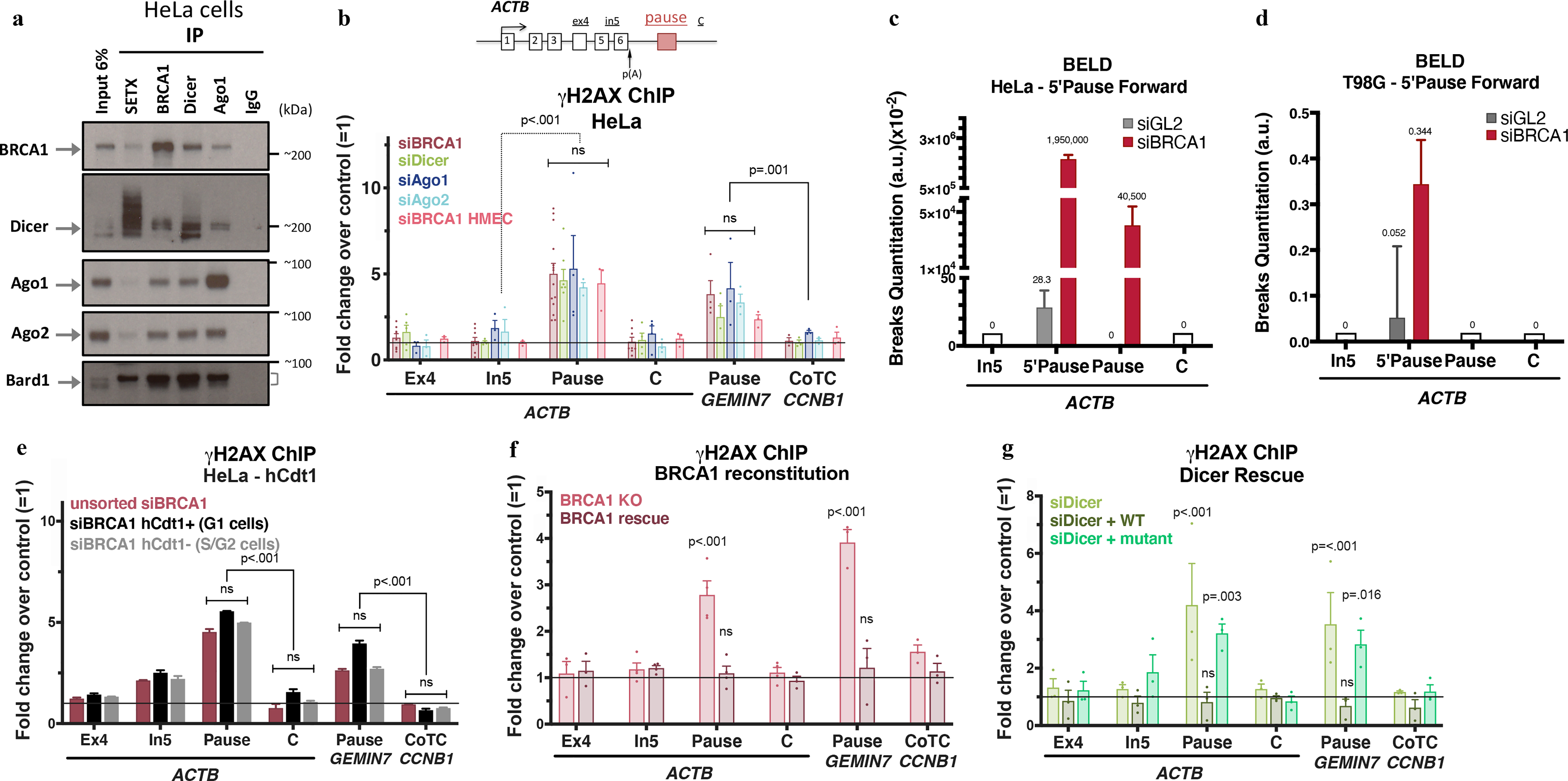
a, Immunoblots from co-IP of endogenous SETX, BRCA1, Dicer, or Ago1 present in nuclear extracts (NE) of HeLa cells. IgG, negative control; Cyt, cytoplasm; NS, Nuclear Soluble; Chrom, chromatin. n=7 b, DNA damage quantitation analysis using γ-H2AX ChIP qPCR analyses following the indicated depletion relative to mock siRNA. ACTB primer location is shown on the scheme. R-loop-positive pause sites (ACTB and GEMIN7) or R-loop-negative (CCNB1 CoTC). Error bars denote s.e.m. (n = 3–14 biological replicates). c-d, BELD quantitation on the ACTB pause site forward/coding strand in HeLa (c) and T98G cells (d). Average relative abundance of qPCR replicates ± s.d are shown. e, Cell cycle- dependent analysis of γ-H2AX ChIP signals in HeLa FUCCI cells. The histograms depict average fold changes of the qPCR replicates ± s.d. f-g, DNA damage analyses in BRCA1 (h) or Dicer (i) rescue experiments, showing average ChIP signals ± s.e.m. (n=3–4 biological replicates). Data were all analyzed by Two-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD (except for f, one-way) and compared to data from the undamaged locus, or relevant control cells.
