Extended Data Figure 8 |. PalB2 binding affinity for sdRNA is independent of Dicer or Ago1/2, but the recruitment of PalB2 and Rad52 to pause sites was, respectively, Rad52- and PalB2-dependent.
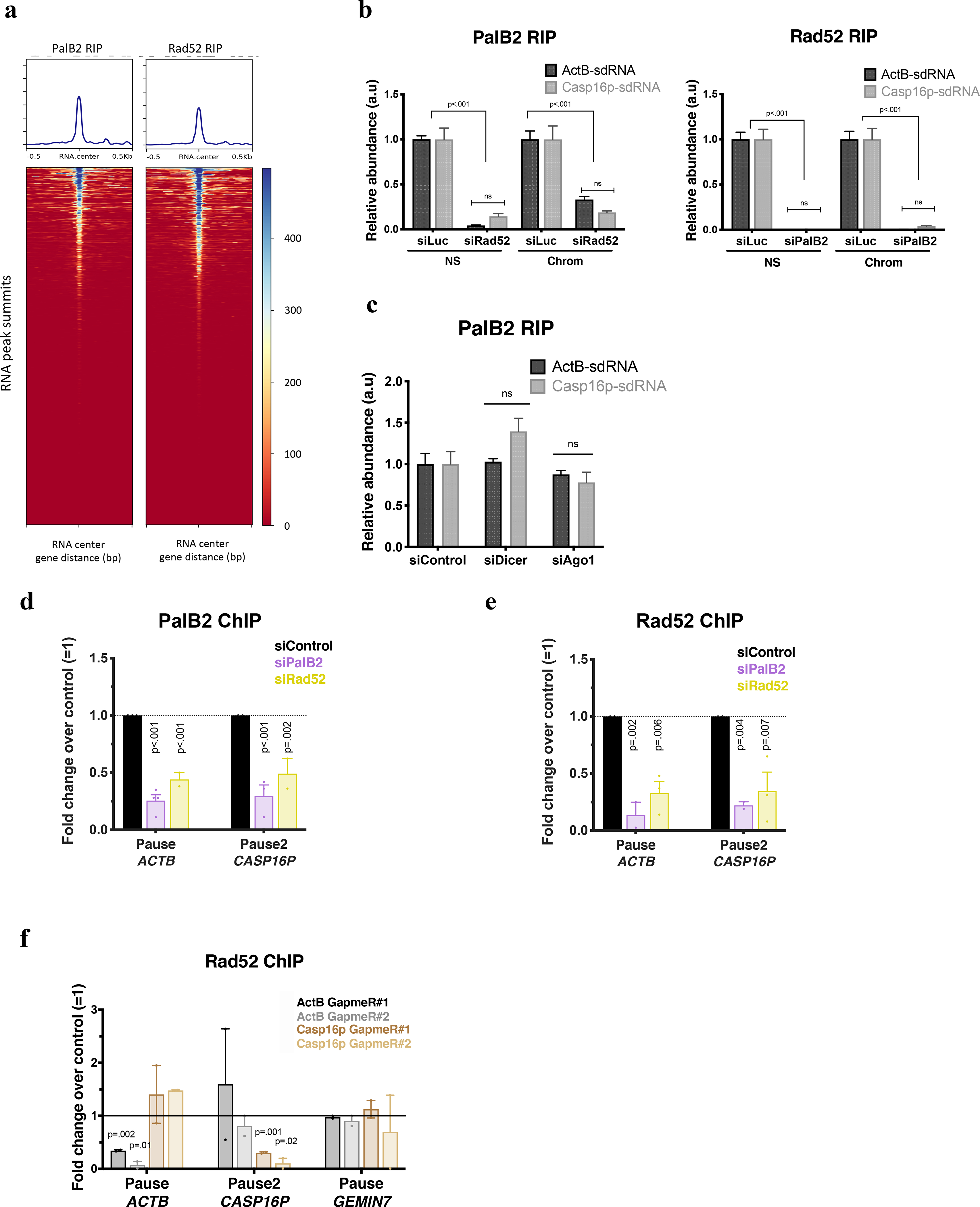
a, PalB2 and Rad52 genome wide RNA ImmunoPrecipitation (RIP) analyses of small RNAs, are shown as heat maps centered around the sdRNA peaks identified in Fig. 2. b, PalB2 and Rad52 RIP analyses of ActB- and Casp16p-sdRNA binding. Representative experiment showing qPCR replicates ± s.d. NS, Nuclear Soluble; Chrom, chromatin. c, Representative RIP analysis showing the relative abundance of PalB2-bound ActB- or Casp16p-sdRNAs (quantified by Taqman and RT-qPCR) after depletion of Dicer or Ago1. d-e, PalB2 (d) and Rad52 (e) ChIP analyses showing ChIP antibody specificity as well as how PalB2 or Rad52 recruitment is influenced following PalB2 or Rad52 depletion (n=2–4 and n=2–3 biological replicates, respectively for PalB2 and Rad52 ChIP). f, Rad52 ChIP analyses with or without depletion of GapmeR-directed ActB- or Casp16p-sdRNA. Data were analyzed by One-way (b-c) or Two-way (d-e) Anova with post-hoc Tukey HSD or multiple t-test (f) and compared to the relevant control cells. ns= non significant.
