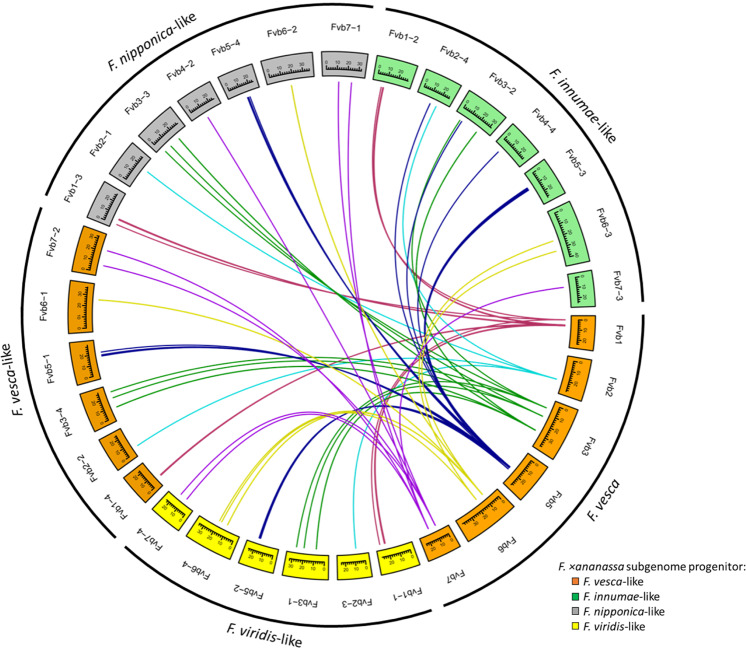
Fig. 3. Synteny analysis of MLO genes between F. vesca and F. ×ananassa. Syntenic regions present in each chromosome of F. vesca were filled with red, light blue, green, dark blue, yellow, and purple sequentially.
A total of 68 connecting lines between two genomes denote syntenic chromosomal regions. The F. vesca chromosomes are highlighted in orange while F. ×ananassa subgenomes were highlighted according to their diploid progenitors namely F. viridis (yellow), F. vesca (orange), F. nipponica (gray) and F. iinumae (green). Chromosomes Fvb4 from F. vesca, and Fvb4–1 and Fvb4–3 from F. ×ananassa, were not included since no putative MLO genes were identified in those regions. The relative chromosome size was indicated by the unit, Mbp. Circular visualization of syntenic regions between F. vesca and F. ×ananassa was constructed using an R-package “Circlize”.