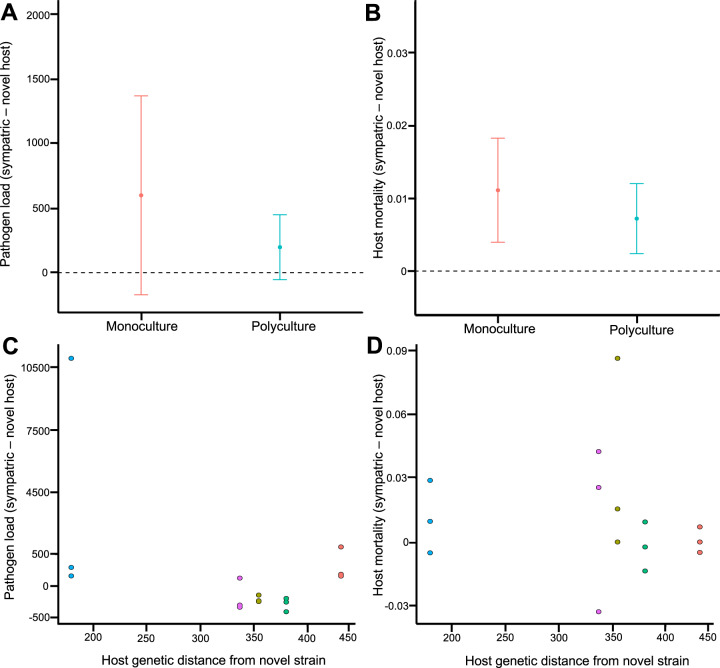
Fig. 4. Maintenance of broad host range in evolved pathogens.
Measurements of pathogen performance in host population genetic backgrounds were taken for (A) pathogen infection load (cfu/host) and (B) host mortality (% proportion of dead in population) in five replicate populations of monoculture-evolved (Red) and polyculture-evolved (Blue) S. aureus. (C) Infection load and (D) pathogen-induced host mortality were not a function of genetic distance between sympatric and novel host genotypes. Host genetic distances were calculated by measuring the Euclidean distances between isolates. Degree of specialism was measured by subtracting the infection metrics in novel (CB4857) hosts from those in sympatric hosts (Kawecki and Ebert [61], Morley et al. [41]), where by 0 (dotted line) shows no difference and a broad host range. The novel host genotype was used for both monoculture and polyculture comparisons. Points show mean ± SE of five technical replicates for (A, B) and three for (C, D).