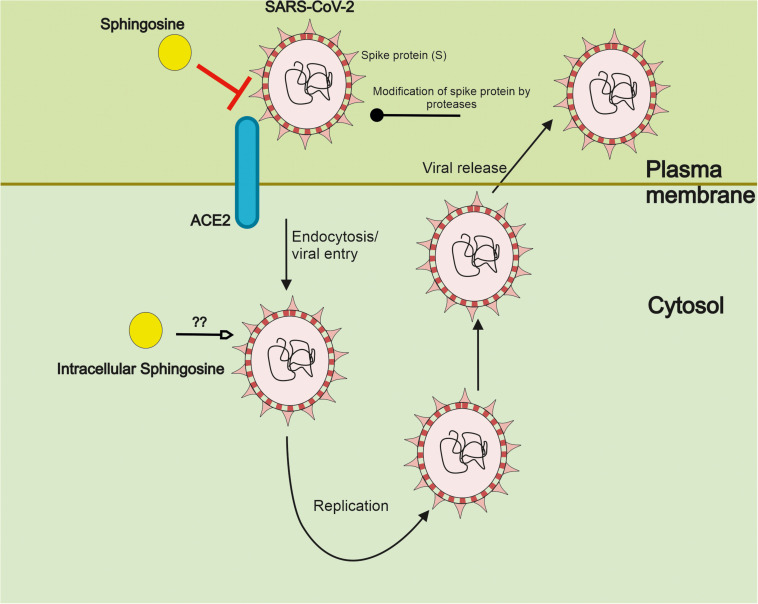
FIGURE 2.
Sphingosine inhibits the interaction of SARS-CoV-2 with its ACE2 receptor. SARS-CoV-2 interacts with its ACE2 receptor on the cell surface via the spike protein (S). Following activity of cell surface protease, the virus is taken up into the cells by membrane fusion events and endocytosis. Subsequent steps in the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 include viral replication and packaging with the release of new particles to infect further cells. Recent studies employing pseudoviral particles of SARS-CoV-2 indicate that sphingosine can bind ACE2 hindering the interaction of the S protein with the receptor in human epithelial cells. This results in a reduced cell entry and probably infectivity of SARS-CoV-2. Sphingosine and sphingolipids are abundantly present in cell membranes. Sphingosine is here depicted in a schematic way but with the caution that it is not a compound in the classical sense of soluble drug interactions. It remains to be shown whether intracellular sphingosine may influence SARS-CoV-2 at other steps also following viral uptake.