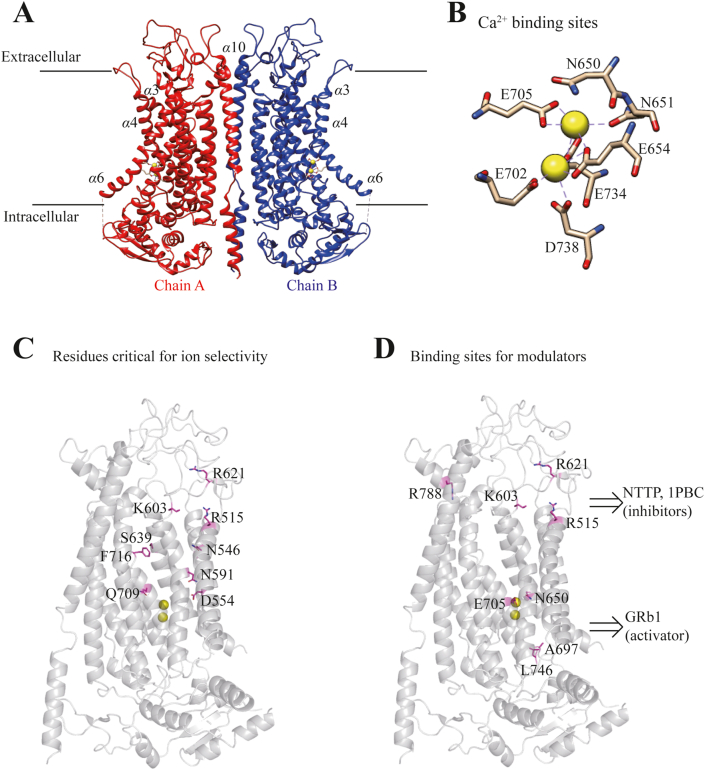
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of ANO1/TMEM16A channel. (A) The Ca2+-bound structure of mANO1 channel in dimer (chains A and B), and 2 yellow filled circles for Ca2+ in each monomer containing 10 transmembrane α helices. (B) Ca2+ binding sites formed by residues N650, N651, E654 from α6, E702, E705 from α7, and E734, D738 from α828,27. (C) Residues critical for ion selectivity including R515 from α3, N546, D554 from α4, N591, V599 from α5, K603, R621 from α5–6 linker, S639 from α6, and Q709, F716 from α726,28. (D) Putative binding sites, R515 from α3, K603, R621 from α5–6 linker, and R788 from α8, for ANO1 inhibitors NTTP and 1PBC26; and N650 from α6, A697, E705 from α7, and L746 from α8 for ANO1 activator GRb129. The structure is regenerated based on the cryo-EM structure of ANO1 channel (PDB 5OYB)27. The residue number labeling is based on the sequence of mTMEM16A (ac) isoform (UniProt Q8BHY3.2).