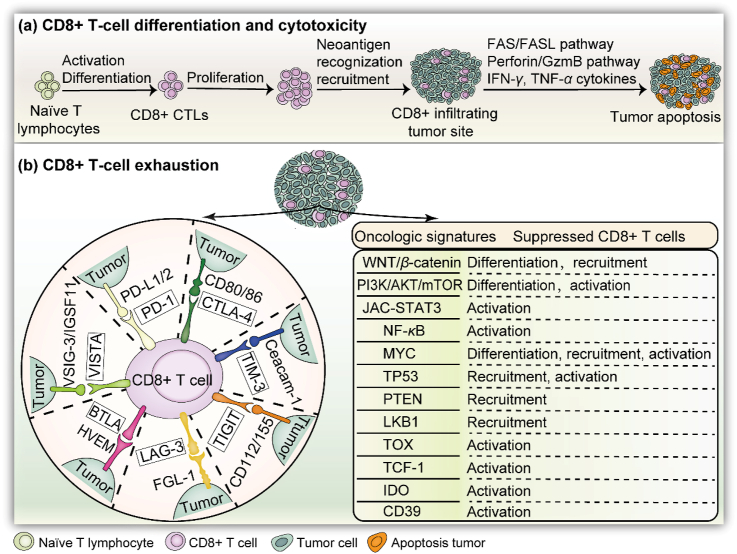
Figure 1.
Infiltration of CD8+ T cells into tumors: differentiation, cytotoxicity, and dysfunction. (a) CD8+ T cells are programmed into CTLs after their activation and proliferation within the TME. The tumor cells are eventually eliminated, depending on IFN-γ and TNF-α secretion and apoptosis pathways. (b) Left: Various immune checkpoints in the divided region involved in CD8+ T cell dysfunction. Once the related ligand–receptor bindings are activated, CD8+ T cells are disabled and lose killing efficacy. Right: Oncologic signatures for suppressing tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. Alternatively, WNT/β-catenin inhibits the differentiation and recruitment of CD8+ T cells against tumors. Other pathways include PI3K, STAT3, NF-κB, MYC, TP53, PTEN, LKB1, TOX, TCF-1, IDO, and CD39.