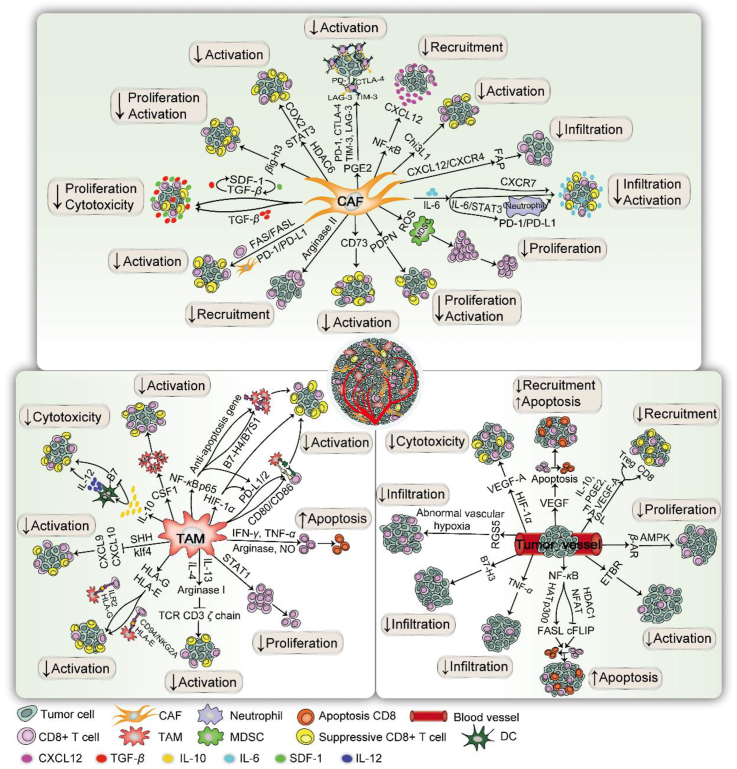
Figure 2.
Suppressive immunization regulation of CD8+ T cells with stromal cells in the TME. The suppressive immunization regulation of CD8+ T cells for pro-tumoral microenvironment with TME-related stromal components is depicted in three parts: CAFs, TAMs, and tumor vessels. (1) For CAFs, the immune checkpoint molecules CTLA-4, TIM-3, PD-1, LAG-3, and CD73 are induced to attenuate CD8+ T cells. NF-κB prevents CD8+ T cells by upregulating CXCL12. IL-6 is secreted to downregulate CD8+ T cell infiltration and IL-6/STAT3 can master the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway to impair T cells by upregulating CXCR7. Tumor-specific CD8+ T cells are inhibited by TGF-β, along with two auto-stimulatory signaling of TGF-β and SDF-1. The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis induces FAP to diminish CD8+ T cells. FAS/FASL on T cells leads to CD8+ T cell apoptosis. CD8+ T cells are excluded with HDAC6 to activate STAT3 by targeting COX2. CAF-driven ROS, Chi3L1, βig-h3, and arginase II are capable of impairing CD8+ T cell activity. (2) For the TME, the immune checkpoint pathways PD-1/PD-L1/2 and CTLA-4/CD80/86 are observed on TAMs to confine CD8+ T cell initiation. NF-κB P65 is validated to impair CD8+ CTLs by inducing B7–H4/B7S1 and anti-apoptosis gene, as well as activating PD-1. Arginase and NO activity are modulators responsible for CD8+ T cell apoptosis via IFN-γ and TNF-α. IL-10 limits cytotoxic CD8+ T cells by suppressing DC-driven IL-12 or selectively reducing B7 upregulation. In addition, STAT1, CSF1, HLA-G, HLA-E, arginase I, and SHH from macrophages are crucial regulators to deplete the CD8+ T cell response. (3) During neovascularization, VEGF inhibits CD8+ T cell homing and induces apoptosis. HIF-1α may modulate vascularization via VEGF-A. FASL is selectively expressed in tumor-driven vasculatures to hinder CD8+ T cells with soluble VEGF-A, IL-10, and PGE2. NF-κB is capable of activating FASL and downregulating cFLIP for apoptosis. Intratumoral CD8+ T cells are rejected by RGS5, resulting in the formation of abnormal blood vessels and hypoxia. HIF-1α, ETBR, B7–H3 β-AR, PDPN, and TNF-α are also pivotal vascular molecules, impeding CD8+ T cell penetration into tumor sites.