Figure 3.
B-Cell Therapies That Target BCR Modulation and Activation
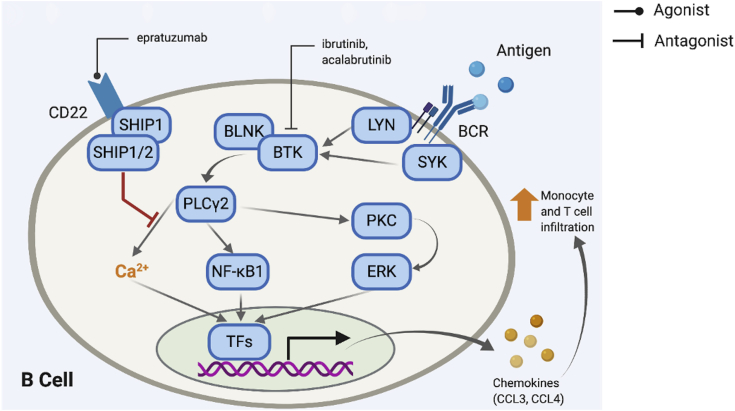
Binding of Ag to the B cell receptor (BCR) induces a signaling cascade that increases intracellular Ca2+ and also results in transcription of genes that increase chemokine release. Ibrutinib and acalabrutinib inhibit BTK, a key step in the cascade, thus possibly decreasing release of chemokines such as CCL3 and CCL4, which enhances tissue infiltration by monocytes and T cells. Similarly, epratuzumab is an agonist of CD22, which, when activated, results in inhibition of the BCR activation cascade. BLNK = B cell linker protein; BTK - Bruton tyrosine kinase; ERK = extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NF-kB1 = nuclear factor kappa Beta subunit 1; PKC = protein kinase C.