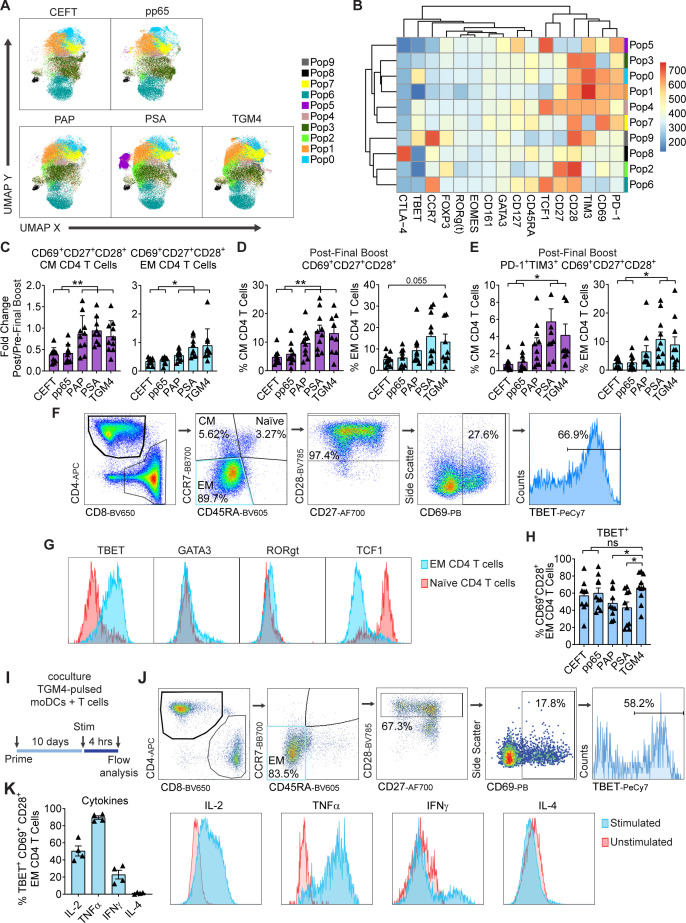
Figure 5.
TGM4 induces CD4 T-cell activation and expansion in vitro. (A) Differential expression of functional markers on expanded populations of CD4 T cells following coculture with autologous protein-pulsed moDCs. Heatmap showing unsupervised clusters determined with the FlowSOM algorithm as described in the Materials and methods section. (B) Expanded CD4 T-cell populations defined by FlowSOM (in A) were projected onto UMAP space as described in the Materials and methods section. Colors correspond to FlowSOM populations. (C) Fold change on activated CD69+CD27+CD28+ EM CD4 T cells (left) and CM CD4 T cells (right) following the last 12 hours of stimulation in expanded T cells. (D) Activated CD69+CD27+CD28+ cells as a percentage of EM CD4 T cells (left) and CM CD4 T cells (right) following in vitro expansion (as in C). (E) PD1+TIM3+ CD69+CD27+CD28+ cells as a percentage of EM CD4 T cells (left) and CM CD4 T cells (right) following in vitro expansion (as in C). (F) Gating strategy used to manually analyze TBET+ in activated CD69+CD28+ EM CD4 T cells defined as CCR7−CD45RA− following coculture with autologous protein-pulsed moDCs. (G) Representative histograms of expression levels of functional transcription factors determined by flow cytometry in expanded EM and naïve CD4 T cells. (H) TBET+ cells as a percentage of activated CD69+CD28+ EM CD4 T cell in expanded T cells (gated as in F). (I) Schematic representation of priming of naïve T cell with autologous TGM4-pulsed moDCs stimulated with PMA/ionomycin 4 hours prior analysis by flow cytometry. (J) Gating strategy used to manually analyze cytokine responses on activated TBET+CD69+CD28+ EM CD4 T cells defined as CCR7−CD45RA− following coculture with autologous TGM4-pulsed moDCs stimulated with PMA/ionomycin. (K) Cytokine production as a percentage of activated TBET+CD69+CD28+ EM CD4 T cells in expanded T cells (gated as in I). Unpaired t-tests performed; *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01. CEFT, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, influenza virus and clostridium tetani; CM, central memory; EM, effector memory; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IL, interleukin; moDC, monocyte-derived dendritic cell; ns, not statistically significant; PAP, prostatic acid phosphatase; PSA, prostate-specific antigen; TGM4, transglutaminase 4.