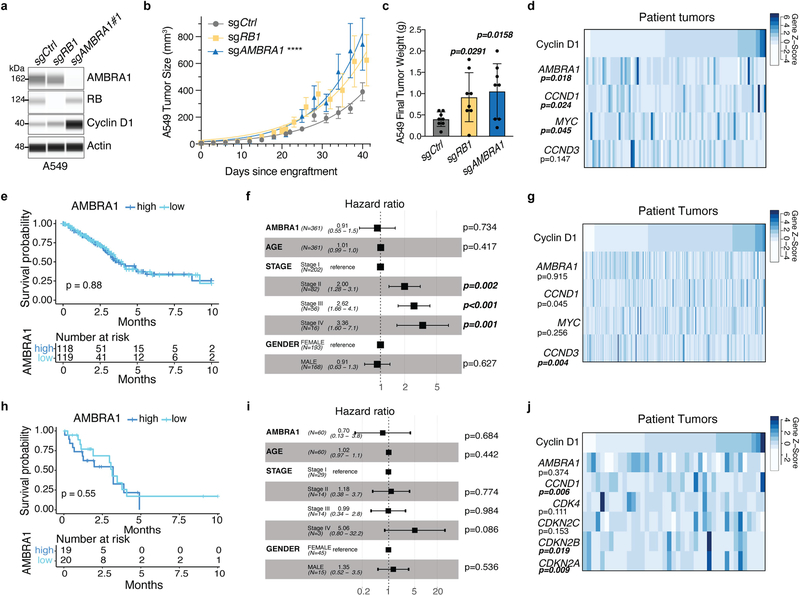
Extended Data Fig. 10 |. AMBRA1 is a tumour suppressor in KRAS-mutant human lung adenocarcinoma.
a, Immunoassay of AMBRA1, RB and cyclin D1 in control and knockout human A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells. Actin is a loading control. b, Growth of control and mutant A549 xenografts in NOD-SCID-gamma (NSG) mice (n = 8 tumours per sgRNA). ****Pinteraction < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA comparing the AMBRA1-knockout curve with control. Tumour volume measurements for RB1-knockout tumours were staggered 1 d behind control and AMBRA1-knockout tumours, which precludes two-way ANOVA. Data are mean ± s.e.m., with best-fit curves for exponential growth. c, Final tumour weights from b. Each symbol is one tumour (n = 8 per sgRNA). Data are mean ± s.d. d, g, j, Cyclin D1 protein levels as measured by reverse phase protein array in relation to the mRNA expression as measured by RNA sequencing (upper quartile of fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM-UQ)) of RB pathway genes that best predict cyclin D1 protein in TCGA KRAS G12-mutant lung adenocarcinoma (d) (n = 90 samples), KRAS wild-type lung adenocarcinoma (g) (n = 257 samples) and EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma (j) (n = 41 samples), using a step-wise regression model. For g, j, AMBRA1 was not selected in the final model but is shown for comparison. Each column is an individual sample, and samples are sorted by cyclin D1 protein levels. e, h, Kaplan–Meier plot of AMBRA1 expression (high, upper third; low, bottom third) in TCGA KRAS wild-type lung adenocarcinoma (e) (n = 361 patients) and EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma (h) (n = 60 patients). f, i, Forest plot of Cox proportional hazard model of TCGA KRAS wild-type lung adenocarcinoma (f) (n = 340 patients) and EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma (i) (n = 60 patients). Model is adjusted by stage, age and gender. P values calculated by two-way ANOVA (b), two-sided unpaired t-test (c), F-test (d, g, j), log-rank test (e, h) and Wald test (f, i).