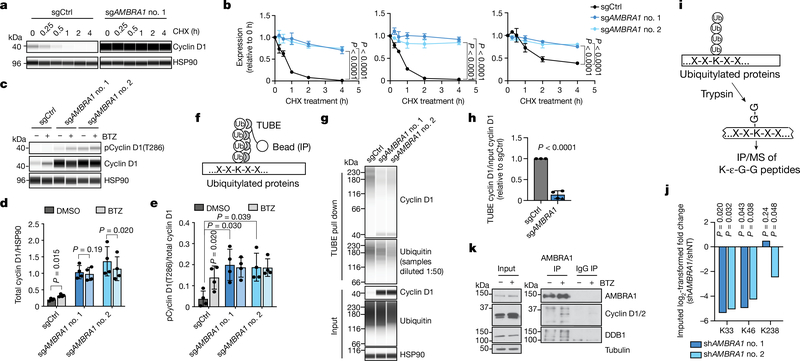
Fig. 2 |. AMBRA1 regulates the stability of cyclin D.
a, Immunoassay of cyclin D1 in control and AMBRA1-knockout U2OS cells treated with 10 μg ml−1 translation inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX) for 0 to 4 h. b, Quantification of cyclin D1 (left), cyclin D2 (middle) and cyclin D3 (right) levels as in a (n = 3 biological replicates). c, Immunoassay of cyclin D1 phosphorylated at T286 and total cyclin D1 in U2OS cells treated with 1 μM proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (BTZ) for 4 h. d, e, Quantification of cyclin D1 (d) and cyclin D1 phosphorylation at T286 (e) in cells from c (n = 4 biological replicates). f, Schematic of the tandem ubiquitin binding entities (TUBE) assay to immunoprecipitate ubiquitylated proteins. g, Immunoassay of ubiquitylated cyclin D1 isolated from U2OS cells using TUBEs. h, Quantification of cyclin D1 ubiquitylation relative to total cyclin D1 from g (n = 3 biological replicates). Data from both AMBRA1 sgRNAs are pooled. Only data from samples with similar levels of ubiquitin pull down are shown. See Supplementary Table 9 for all data. i, Schematic of mass spectrometry (MS) analysis to detect ubiquitylated proteins after immunoprecipitation with anti-K-ε-G-G antibodies. j, Quantification of cyclin D1 ubiquitylation at the three lysines detected by immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry of K-ε-G-G peptides. shAMBRAl no. 1 and no. 2 denote two different short hairpin RNAs (shRNA) against AMBRA1; shNT, non-targeting shRNA. k, Co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous AMBRA1 and cyclin D in U2OS cells pretreated with 1 μM bortezomib for 4 h, analysed by immunoblot. DDB1 is a positive control for AMBRA1 binding. The cyclin D antibody recognizes cyclin D1 and D2. Representative of two independent experiments. HSP90 and tubulin are loading controls. All data are mean ± s.d. P values calculated by two-way ANOVA (b), two-sided t-test (paired t-test for d, e; unpaired t-test for h), and two-sided unpaired t-test with Benjamini–Hochberg correction (j).