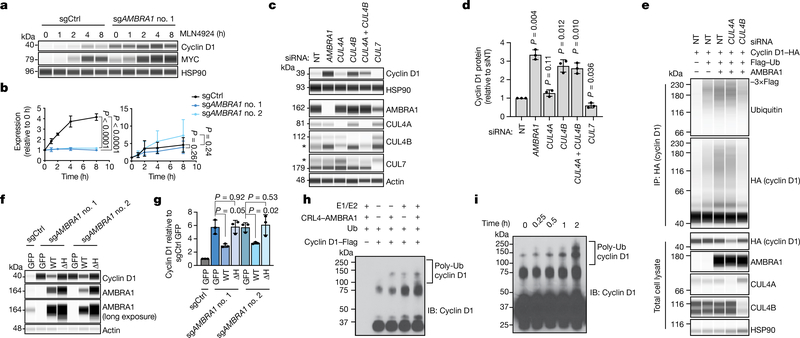
Fig. 3 |. CRL4AMBRA1 ubiquitylates cyclin D.
a, Immunoassay of cyclin D1 and MYC in U2OS cells treated with 1 μM neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 for 0 to 8 h. b, Quantification of a (n = 3 biological replicates). Left, cyclin D1; right, MYC. c, Immunoassay of cyclin D1 in U2OS cells following knockdown of AMBRA1 or various cullin proteins. Asterisk, nonspecific band. The CUL4B antibody appears to cross-react with CUL4A. d, Quantification of cyclin D1 in c (n = 3 biological replicates). e, Immunoassay of cyclin D1 ubiquitylation in 293T cells following overexpression of AMBRA1 and knockdown of CUL4A or CUL4B. Cells were pretreated with 1 μM bortezomib for 3 h. Representative of two independent experiments. f, Immunoassay of cyclin D1 and AMBRA1 in U2OS cells with doxycycline-inducible wild-type AMBRA1 (WT), AMBRA1(ΔH) (ΔH) or GFP control, treated with 500 ng ml−1 doxycycline for 2 d. g, Quantification of cyclin D1 in f (n = 3 biological replicates). h, Immunoblot of cyclin D1 polyubiquitylation (poly-Ub) from in vitro ubiquitylation assays performed on purified cyclin D1. AMBRA1 and CUL4B (CRL4–AMBRA1) were independently purified from 293T cells, and E1, E2 and ubiquitin (Ub) are recombinant proteins (n = 1 experiment). i, Immunoblot of cyclin D1 polyubiquitylation from in vitro ubiquitylation time-course assays, similar to h. Representative of two independent experiments. HSP90 and actin are loading controls. All data are mean ± s.d. P values calculated by two-way ANOVA (b) or two-sided paired t-test (d, g).