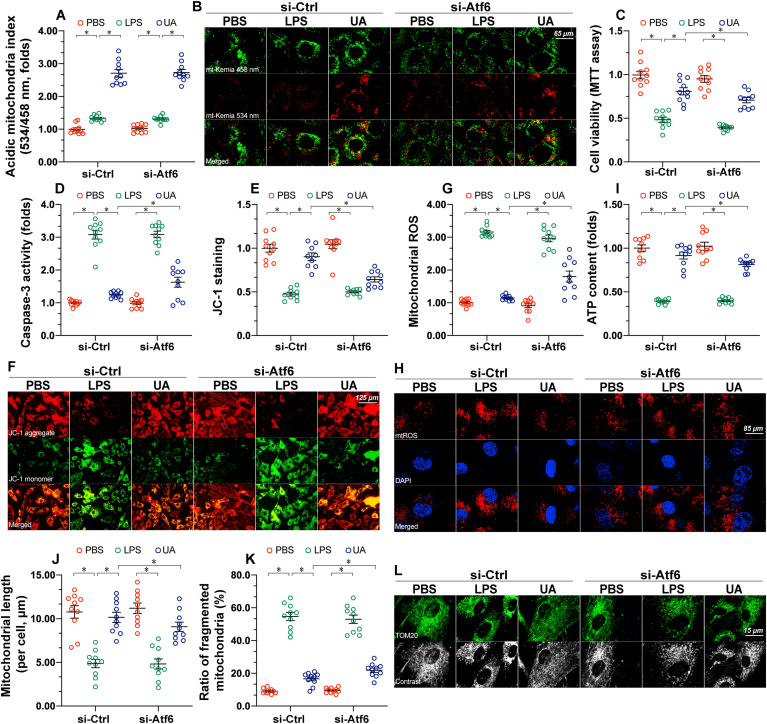
Fig. 5.
Inhibition of UPRmtpartly abolishes the cardioprotective effect of mitophagy activation. The AC16 human ventricular cardiomyocyte cell line was treated with 10 μg/mL of LPS to induce sepsis-related cardiomyocyte damage. UA, an inducer of mitophagy, was used to culture AC16 cells. siRNA against FUNDC1 (si-FUNDC1) and Atf6 (si-Atf6) were transfected into AC15 to inhibit the activation of mitophagy and UPRmt, respectively. A-B. Mitophagy activity was observed using the mt-Keima assay. A yellow signal highlights increased mitophagic flux within cardiomyocytes. C. Cell viability was determined using an MTT assay. D. ELISA analysis of caspase-3 activity. E-F. AC16 cells were stained with JC-1 to observe changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential. G-H. AC16 cells were stained with the MitoSOX red mitochondrial superoxide indicator to show changes in mitochondrial ROS. I. Total ATP production was determined using the Cell Titer-Glo Luminescent Viability assay. J-L. Mitochondrial morphology was revealed using confocal immunofluorescence. TOM20 was used to show the shape of mitochondria in response to LPS or FUNDC1 deletion. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, normalized per 1000 cardiomyocytes. *P<0.05. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)