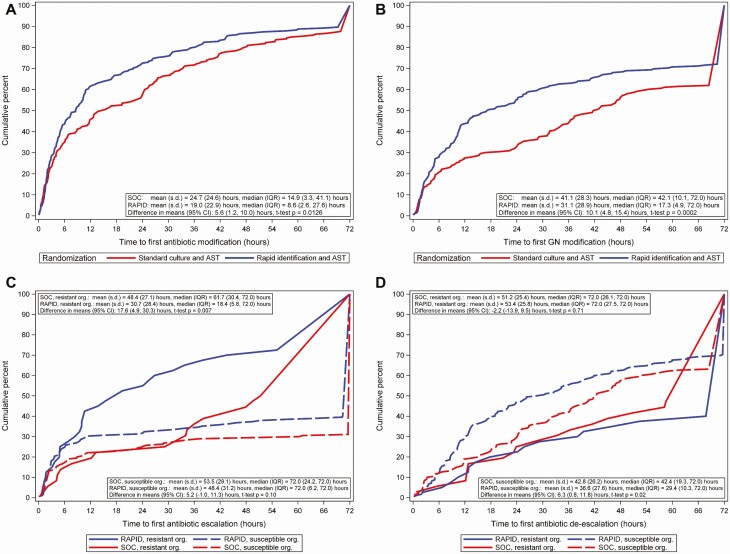
Figure 2.
Time from randomization to antibiotic changes by treatment arm in the modified intention-to-treat population. A, Time from randomization to first antibiotic modification by treatment arm. For patients who died within 72 hours, the time of earliest antibiotic modification was used as the time to modification. Patients who did not have antibiotic modifications were assigned a time of 72 hours. No censoring was observed. Includes time to first antibiotic modification for 8 patients who died within 72 hours of randomization. B, Time from randomization to first gram-negative antibiotic modification by treatment arm. Patients who did not have gram-negative antibiotic modifications were assigned a time of 72 hours. Includes time to first gram-negative antibiotic modification for 8 patients who died within 72 hours of randomization. C, Time from randomization to first antibiotic escalation in gram-negative or gram-positive antibiotics by treatment arm and isolate resistance. Resistance is defined as third-generation cephalosporin nonsusceptible Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, or carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas species. Isolates with intermediate susceptibility were considered resistant. Resistant organisms: n = 36 for SOC and 40 for RAPID. Susceptible organisms: n = 190 for SOC and 182 for RAPID. Patients who did not have antibiotic escalation were assigned a time of 72 hours. Antibiotic escalation was assessed by local stewardship providers. D, Time from randomization to first antibiotic deescalation in gram-negative or gram-positive antibiotics by treatment arm and isolate resistance. Resistance is defined as third-generation cephalosporin nonsusceptible Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, or carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas species. Isolates with intermediate susceptibility were considered resistant. Resistant organisms: n = 36 for SOC and 40 for RAPID. Susceptible organisms: n = 190 for SOC and 182 for RAPID. Patients who did not have antibiotic deescalation were assigned a time of 72 hours. Antibiotic deescalation was assessed by local stewardship providers. Abbreviations: AST, antibiotic susceptibility testing; CI, confidence interval; GN, gram-negative; IQR, interquartile range; Org, organism; RAPID, organism identification and phenotypic AST using the Accelerate Pheno System; s.d., standard deviation; SOC, standard-of-care culture.