Figure 4.
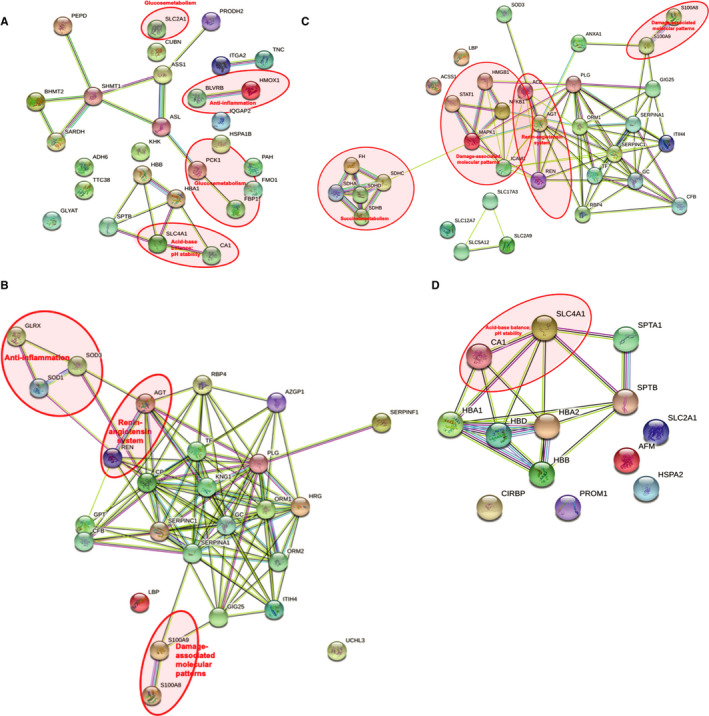
Prolonged NMP with URC drives metabolic homeostasis. (A) Upregulated cellular pathways after 6 hours NMP with URC. Acid–base balance and pH stability: CA1 carbonic anhydrase 1; SLC4A1 band 3 anion transport protein. Glucose metabolism: PCK1 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; FBP1 fructose‐1,6‐bisphosphatase 1; SLC2A1 solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1. Anti‐inflammation: BLVRB flavin reductase (NADPH); broad specificity oxidoreductase that catalyzes the NADPH‐dependent reduction of a variety of flavins, such as riboflavin, FAD or FMN, biliverdins, methemoglobin and PQQ (pyrroloquinoline quinone); contributes to heme catabolism and metabolizes linear tetrapyrroles; can also reduce the complexed Fe(3+) iron to Fe(2+) in the presence of FMN and NADPH. HMOX1 heme oxygenase 1; cleaves the heme ring at the alpha methene bridge to form biliverdin; biliverdin is subsequently converted to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase; exhibits cytoprotective effects since excess of free heme sensitizes cells to undergo apoptosis. (B) Upregulated cellular pathways after 6 hours NMP with UR. Renin–angiotensin system: AGT angiotensinogen; a potent regulator of blood pressure, body fluid, and electrolyte homeostasis. REN renin; to generate angiotensin I from angiotensinogen in the plasma, initiating a cascade of reactions that produce an elevation of blood pressure and increased sodium retention by the kidney. Damage‐associated molecular patterns (DAMPs): S100A8 protein S100‐A8; a calcium‐ and zinc‐binding protein which plays a prominent role in the regulation of inflammatory processes and immune response. It can induce neutrophil chemotaxis and adhesion. Predominantly found as calprotectin (S100A8/A9) which has a wide plethora of intra‐ and extracellular functions. S100A9 protein S100‐A9; a calcium‐ and zinc‐binding protein which plays a prominent role in the regulation of inflammatory processes and immune response. It can induce neutrophil chemotaxis, adhesion, can increase the bactericidal activity of neutrophils by promoting phagocytosis via activation of SYK, PI3 K/AKT, and ERK1/2 and can induce degranulation of neutrophils by a MAPK‐dependent mechanism. Anti‐inflammation: GLRX glutaredoxin 1; has a glutathione‐disulfide oxidoreductase activity in the presence of NADPH and glutathione reductase. SOD1 superoxide dismutase; destroys radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems. SOD3 extracellular superoxide dismutase; protects the extracellular space from toxic effect of reactive oxygen intermediates by converting superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide and oxygen. (C) Downregulated cellular pathways after 6 hours NMP with URC. Renin–angiotensin system: AGT angiotensinogen; ACE angiotensin‐converting enzyme; converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II by release of the terminal His‐Leu, this results in an increase in the vasoconstrictor activity of angiotensin. Also able to inactivate bradykinin, a potent vasodilator. Damage‐associated molecular patterns (DAMPs): HMGB1 high‐mobility group box 1; promotes host inflammatory response to sterile and infectious signals and is involved in the coordination and integration of innate and adaptive immune responses. NFKB1 nuclear factor NF‐kappa‐B p105; a pleiotropic transcription factor; related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis, and apoptosis. MAPK1 mitogen‐activated protein kinase 1; serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. ICAM1 intercellular adhesion molecule 1; ligands for the leukocyte adhesion protein LFA‐1 (integrin alpha‐L/beta‐2). STAT1 signal transducer and activator of transcription 1‐alpha/beta; signal transducer and transcription activator that mediates cellular responses to interferons (IFNs), cytokine KITLG/SCF and other cytokines and other growth factors. S100A8 protein S100‐A8. Succinate metabolism: SDHA/B/C/D succinate dehydrogenase subunits; A= flavoprotein subunit; B= iron–sulfur protein subunit; C and D= membrane anchoring subunits; involved in complex II of the mitochondrial electron transport chain and is responsible for transferring electrons from succinate to ubiquinone (coenzyme Q). FH fumarate hydratase; class II fumarase/aspartate family. (D) Downregulated cellular pathways after 6 hours NMP with UR. Acid–base balance and pH stability: CA1 carbonic anhydrase 1; SLC4A1 band 3 anion transport protein. NMP=normothermic machine perfusion of the kidney. UR=urine replacement. URC=urine recirculation. String Version 11.0; © String Consortium 2020. 22 Lines: line color indicates the type of interaction evidence; Nodes: colored—query proteins and first shell of interactors; white—second shell of interactors; empty—proteins of unknown 3D structure; filled—some 3D structure is known or predicted
