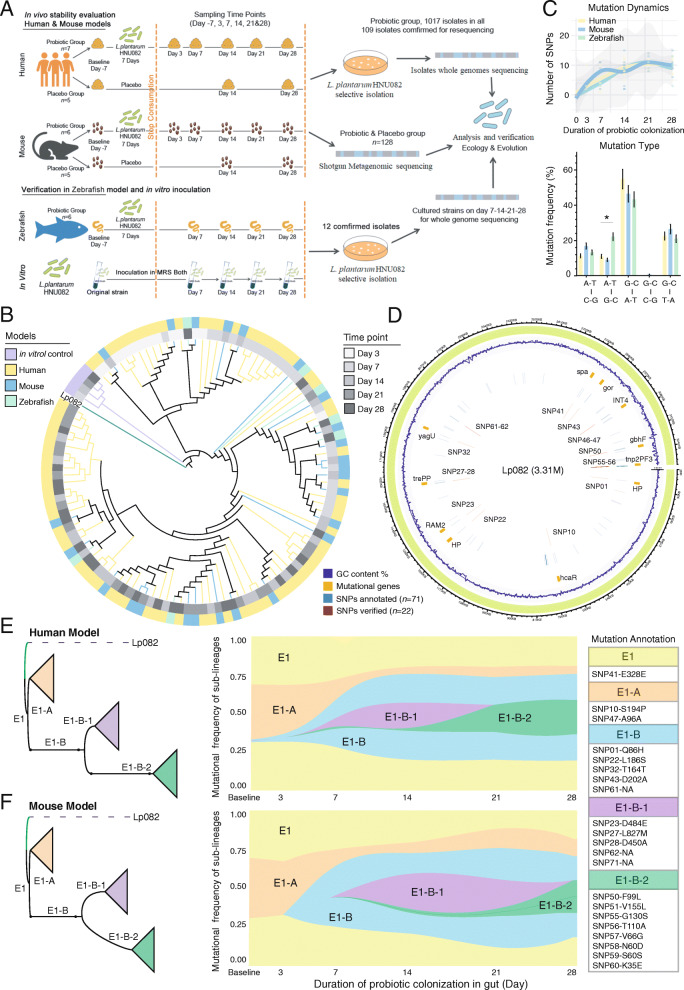
Fig. 1.
The in vivo adaptive evolutionary dynamics of probiotics over a 4-weeks sampling period in the gut of humans, mice and zebrafish. A The experimental design. We used Lp082 as a model probiotic strain to explore the effects of host-derived selection pressure (the mouse and human models were applied; the zebrafish model was used for further verification) on the genetic stability of the ingested probiotics and the impact of probiotic mutations on the indigenous gut microbiome of different hosts (the mouse and human model). First, we sequenced the complete genome of this model probiotic strain. We next isolated the probiotics from the feces of hosts at different time points to identify genetic mutations using whole-genome resequencing. Simultaneously, the original strain was continuously inoculated in vitro and sequenced to assess genetic mutation in the absence of host selective pressure. Next, we employed the metagenomic sequencing method to characterize the impact of probiotics ingestion on resident gut microbiota in humans and mice as compared to the placebo groups. B Phylogenetic tree constructed based on the SNPs of all Lp082 isolates. The different grey bars and color bars represent the strains isolated from different time points and different hosts, and the Lp082 was set as the root strain. The isolates were dominated by 22 SNPs during the probiotic colonization, especially in the first two time points of the human model. C The number of SNPs detected at every sampling time point (including the day 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28) in human, mouse, and zebrafish models (top panel). No significant difference in the number of SNPs at the end of the experiment was found among the three models. The mutation type of G-C to A-T was the most frequently detected in all three models, but the frequency of the mutation type of A-T to G-C was significantly higher in the zebrafish model than that in the other two models (bottom panel). D All confirmed SNPs and their gene locations are marked on the reference genome of Lp082. E, F (left panel) The simplified phylogenetic tree based on Lp082 isolates from the human (E) and mouse (F) model in all sampling time points. The tree is rooted in the ancient probiotic strain consumed and evolved into 3 groups (labeled in different colors) based on 21 SNPs in 5 branches. The evolutionary relationships of the 5 branches are visualized as E1, E1-A/B, and E1-B-1/2. E, F (right panel) The evolutionary dynamics of the 5 branches (in different colors) in the human and mouse model were constructed based on the mutation frequency of the 21 SNPs. A major difference in the evolutionary dynamics of branch E1-B-1 was observed between the human and mouse model, which consisted of the temporary evolutionary divergence in the second week of probiotic colonization