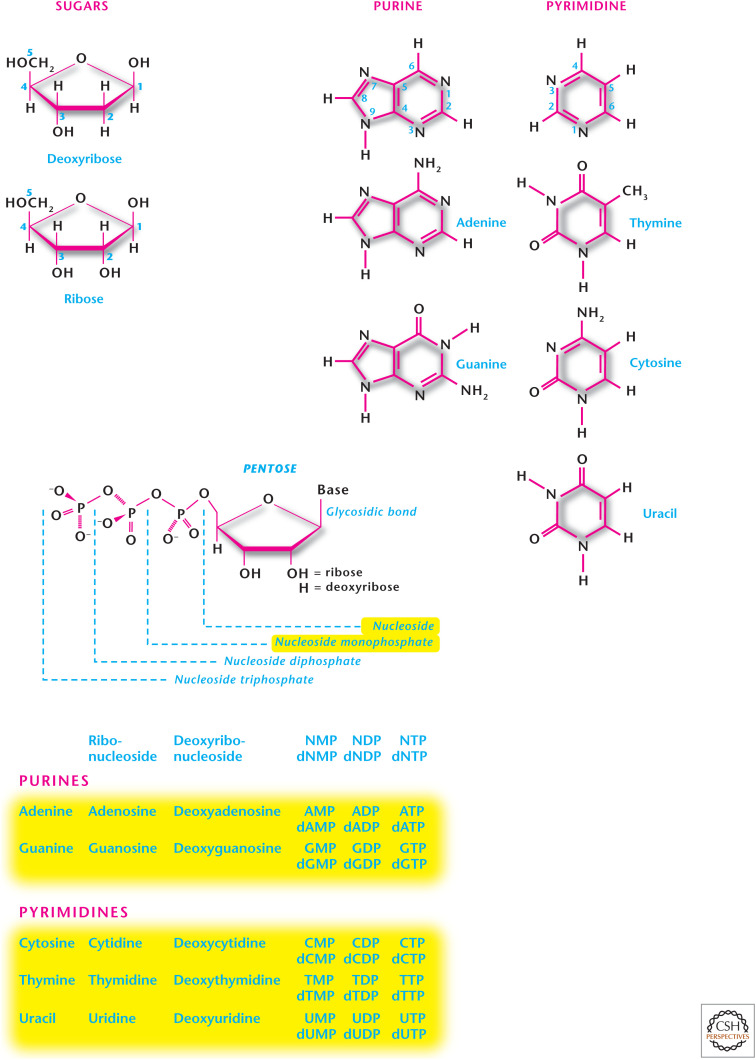
Figure 2.
Structure of purines and pyrimidines. Nucleosides have either a ribose or 2-deoxyribose bound to purine or pyrimidine. The addition of one or more phosphates to a nucleoside results in a nucleotide. Purines (adenine and guanine) are compromised of attached six-membered and five-membered nitrogen-containing rings. Pyrimidines (uracil, thymine, and cytosine) have only a six-membered nitrogen-containing ring.