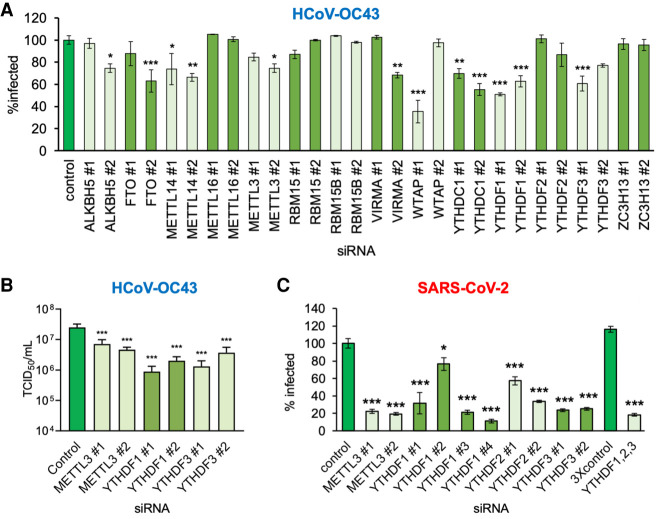
Figure 1.
Focused RNA interference screen implicates METTL3 and the YTHDF readers in control of β-coronavirus replication. (A) Human MRC-5 normal lung fibroblasts were transfected with a set of validated siRNAs (two per factor) targeting 14 host components of the m6A pathway and cultured for 72 h before infection with HCoV-OC43 at MOI = 0.001. After 48 h, cells were fixed and the infection assessed by indirect immunofluorescence using an antibody to the viral nucleocapsid protein (N). The percentage of N-positive cells per well was determined using a CellInsight CX7 LZR high-content screening platform. Each assay was performed three times with technical duplicates and normalized to control siRNA treated cells. (B) The impact of siRNA depletion on infectious viral titer was determined by collecting supernatant culture media from A and establishing TCID50 on MRC-5 cells. (C) A549+ACE2 cells were transfected with validated siRNAs targeting METTL3, YTHDF1, YTHDF2, and YTHDF3, either individually or as a mix of single siRNAs to all three YTHDF proteins using siRNA#1 in each case. After 72 h, the cells were infected with icSARS-CoV-2-mNG at MOI = 0.1 for 48 h and then fixed and scored for green fluorescence. The extent of spread was normalized to cells transfected with control siRNA. In each case, an ANOVA test with Dunnett multiple comparison correction was used to establish statistical significance compared with control siRNA. (*) P < 0.033, (**) P < 0.002, (***) P < 0.001.